Netskope IPSec with Fortinet FortiGate
This guide illustrates how to configure a VPN IPSec tunnel between Netskope and a FortiGate firewall device. This configuration example uses a FortiGate device running FortiOS version 6.4.3. It can work for all FortiOS versions.
There’re two options to accomplish the configuration: CLI and GUI. The CLI is faster.
FortiGate CLI Configuration
Create a VPN for IPsec Phase 1.
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface edit "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" set interface "wan1" << change for your wan interface set ike-version 2 set keylife 28800 set peertype any set net-device disable set mode-cfg disable set proposal aes128-sha256 aes256-sha256 aes128-sha1 aes256-sha1 set localid "XXXXX@XXXXXX" << change for your localid set dhgrp 16 15 14 set remote-gw 163.116.XXXX.38 << change for your selected POP set psksecret XXXXXXX << change for your preshared next endCreate a VPN for IPsec Phase 2.
config vpn ipsec phase2-interface edit "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" set phase1name "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" set proposal aes256gcm aes128gcm aes128-sha1 aes256-sha1 set dhgrp 16 15 14 set auto-negotiate enable set keylifeseconds 7200 next endCreate at least one policy with VPN interface associated.
config firewall policy edit 999 set srcintf "internal" set dstintf "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" set srcaddr "all" set dstaddr "all" set action accept set schedule "always set service "HTTP" "HTTPS" set logtraffic all set nat enable next endCreate a route to push VPN into RIB.
config router static edit 999 set priority 10 set device "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" next endCreate a policy-based router to redirect web traffic to Netskope.
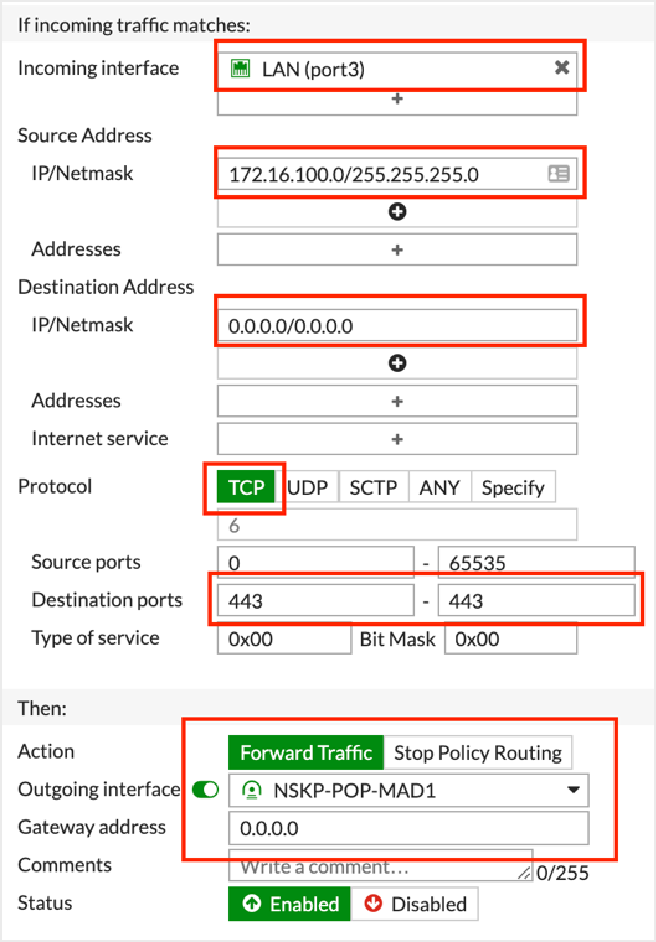
config router policy edit 998 set input-device "internal" << incoming interface set src "172.16.100.0/255.255.255.0" << LAN network set dst "0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0" set protocol 6 set start-port 443 set end-port 443 set output-device "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" next edit 999 set input-device "internal" << incoming interface set src "172.16.100.0/255.255.255.0" << LAN network set dst "0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0" set protocol 6 set start-port 80 set end-port 80 set output-device "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" end
FortiGate GUI Configuration
Click + Create New and then IPsec Tunnel.
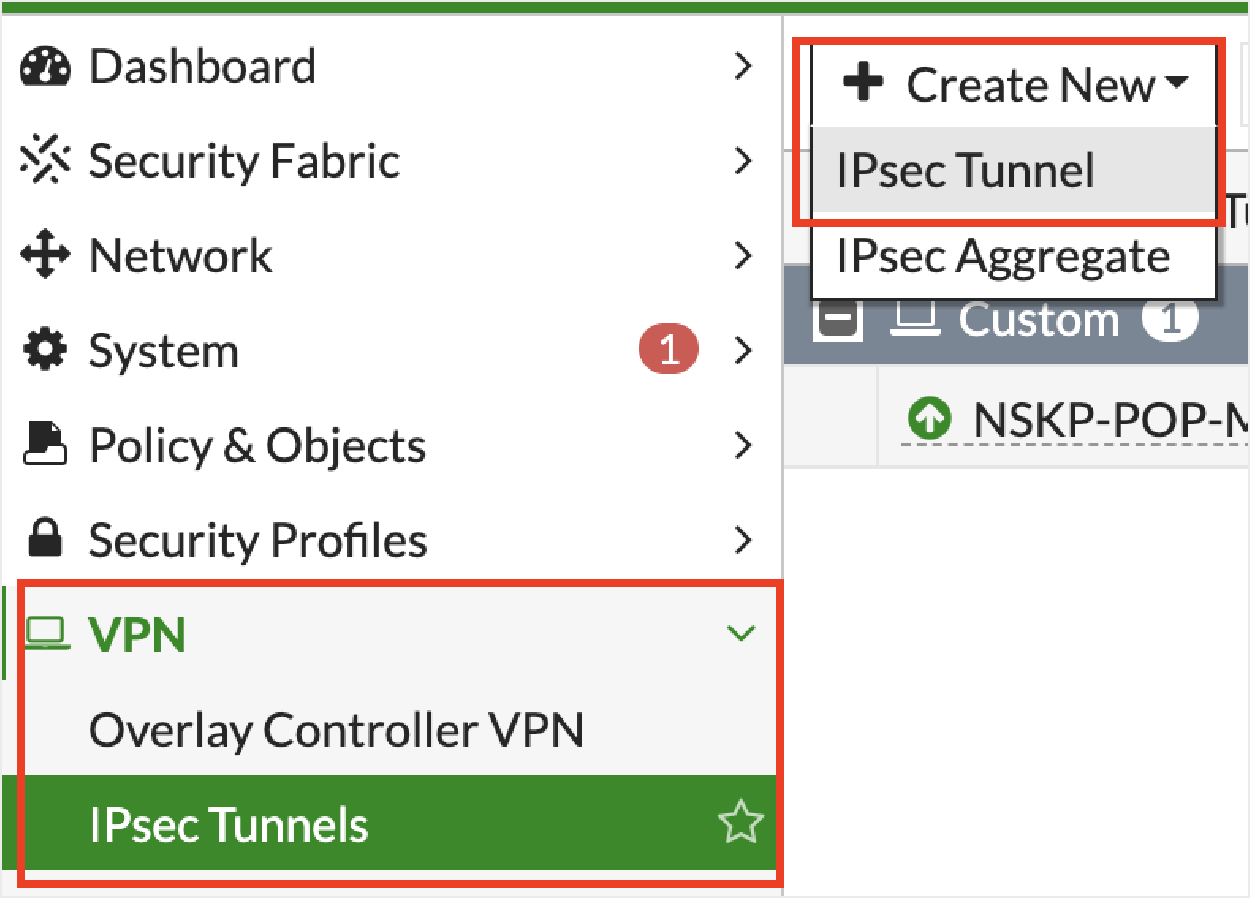
Under VPN Setup:
Name: Enter a name for the tunnel.
Template type: Select Custom.
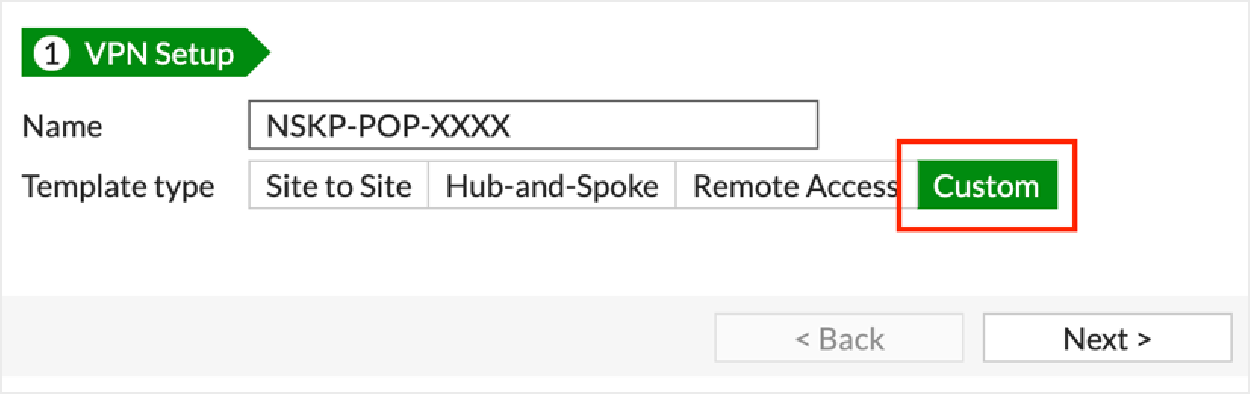
In the Network section, configure the IP address and interface information:
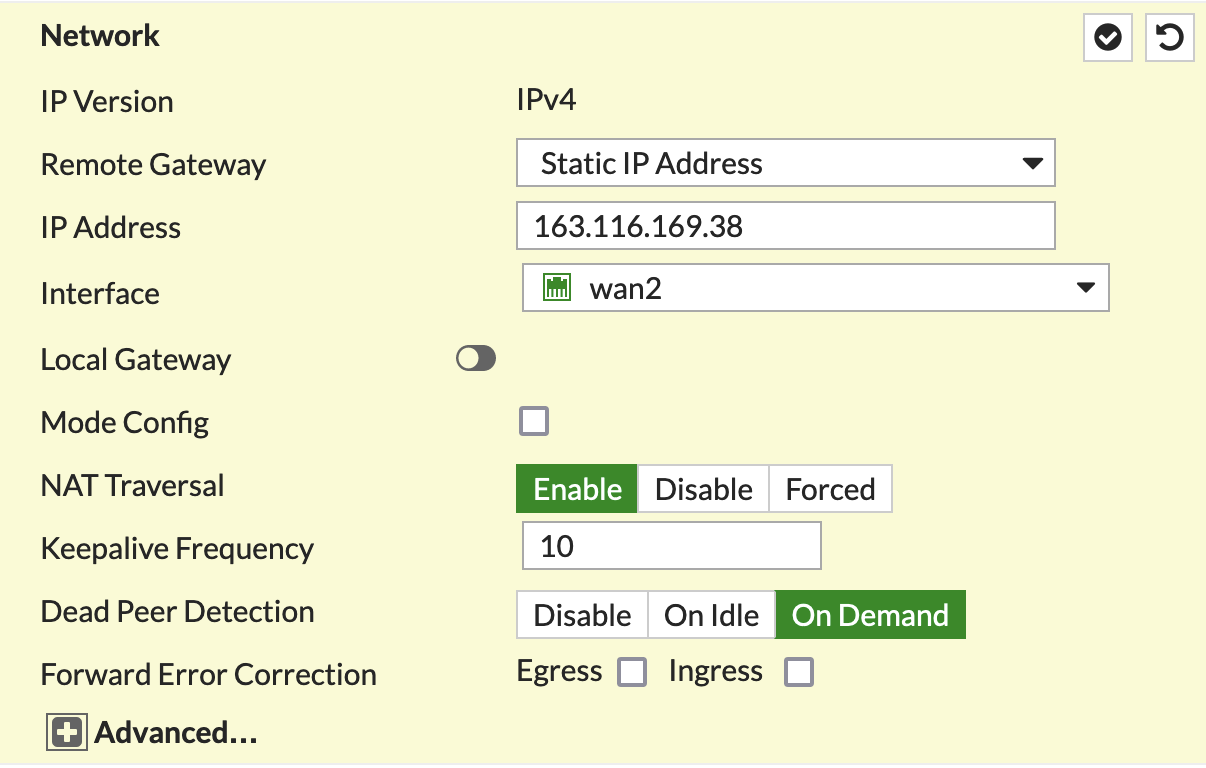
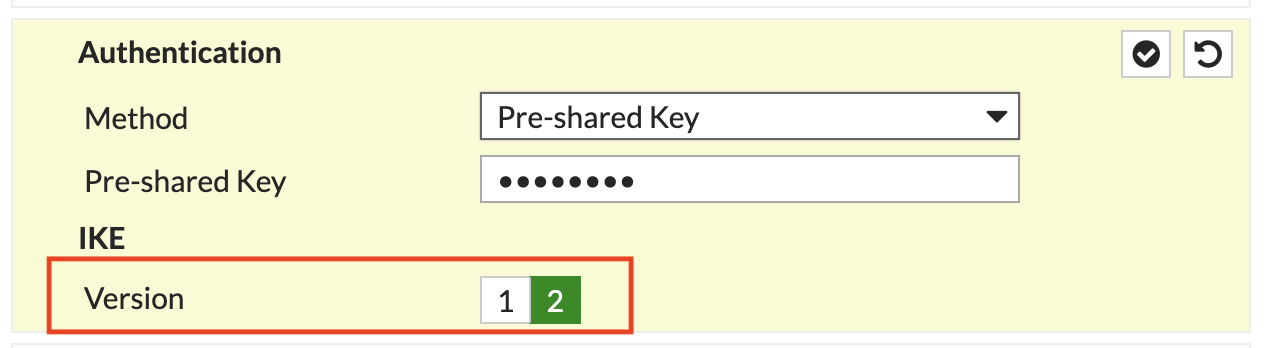
In the Authentication section, configure the pre-shared key and select IKEv2:
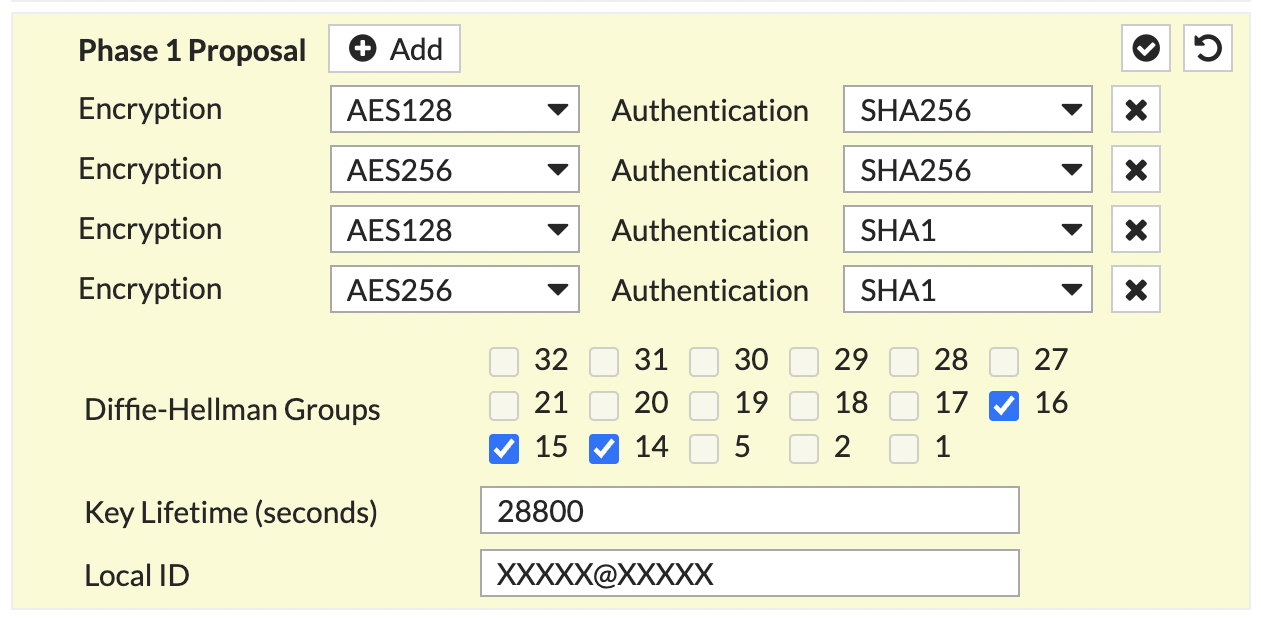
In the Phase 1 Proposal section, configure the following:
Note
The Local ID must be entered.Netskope recommends usingan email format as a local ID, such as xxxx@xxxx.xxx. It must be the same as the source identity in your Netskope tenant.
In the Phase 2 Proposal section, configure the following:
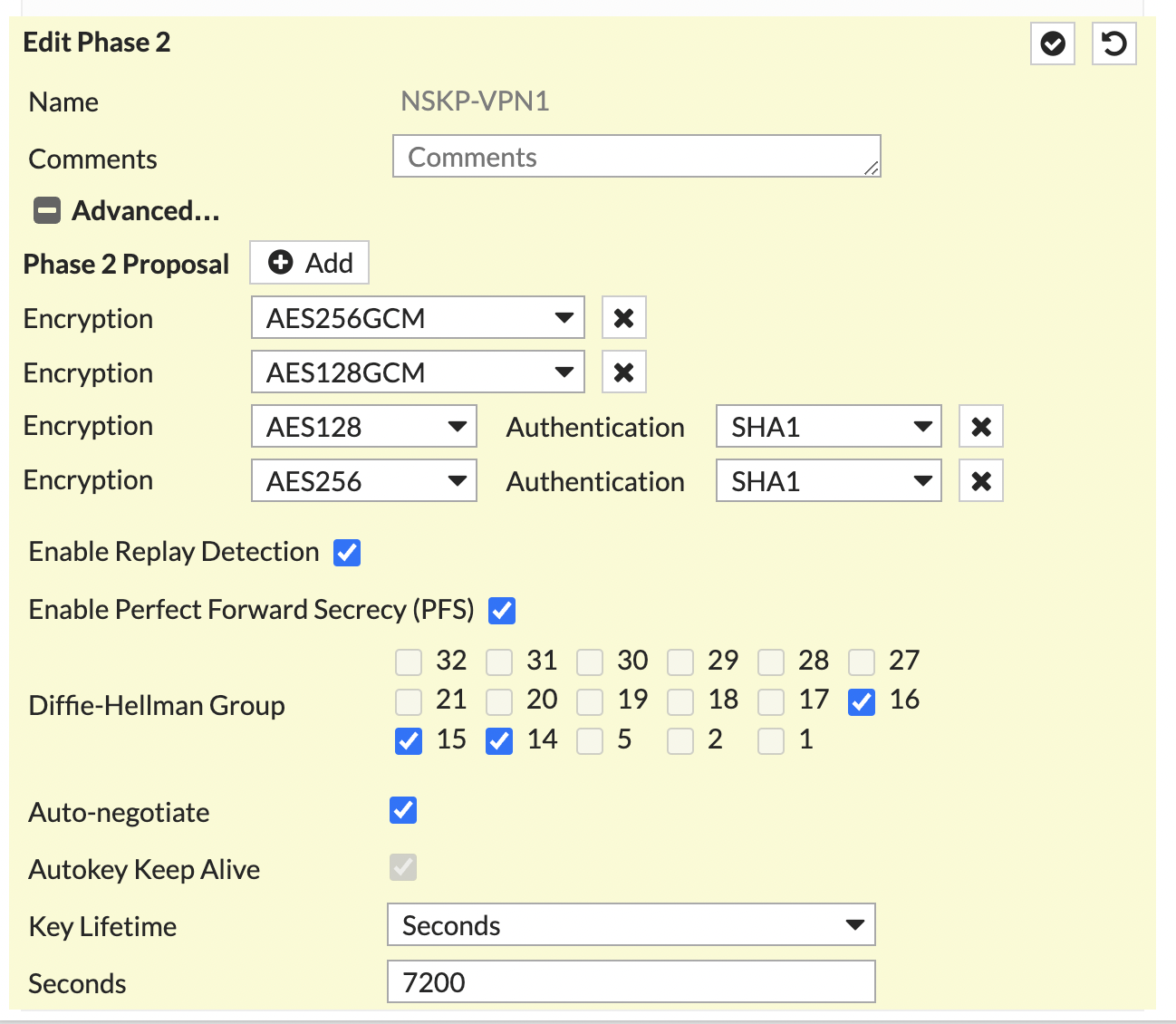
Click OK.
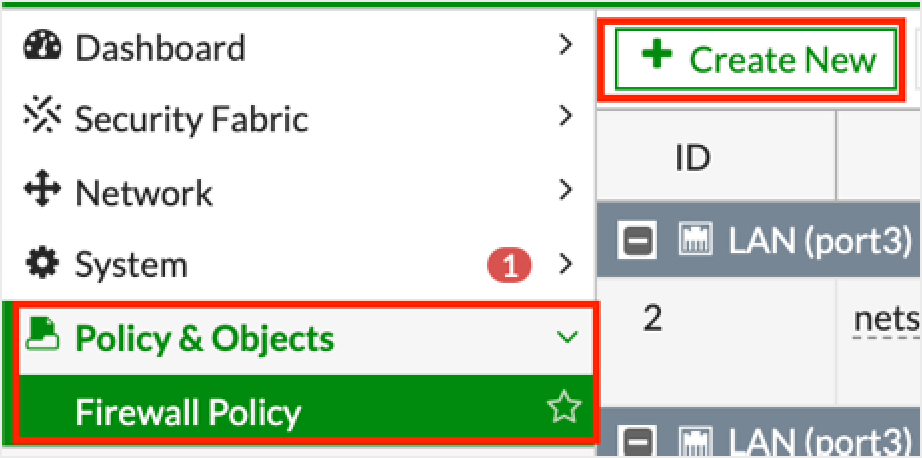
To create at least one policy with a VPN interface associated:
Go to Policy & Objects > Firewall Policy.
Click + Create New.
In the Edit Policy window, configure the following fields:
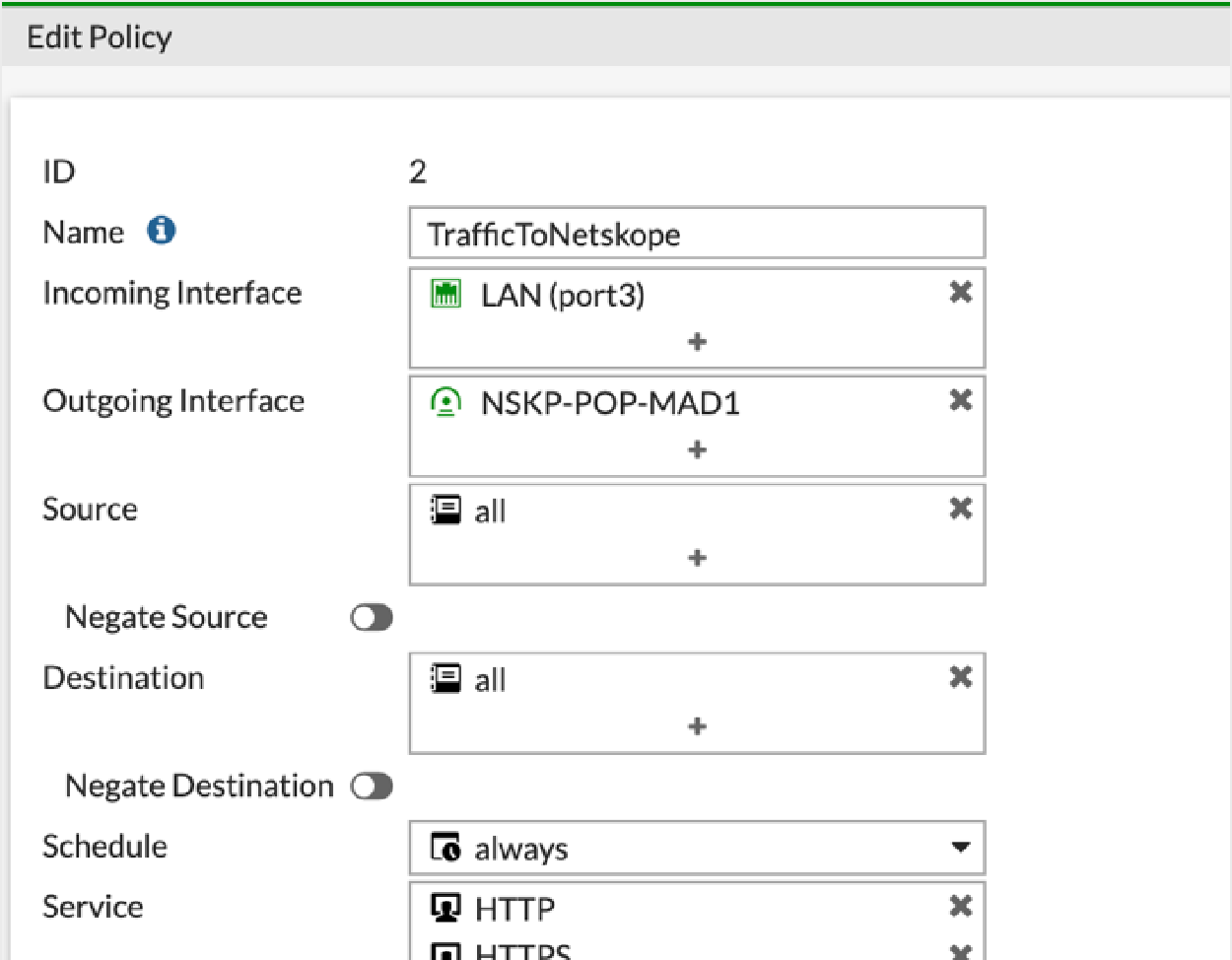
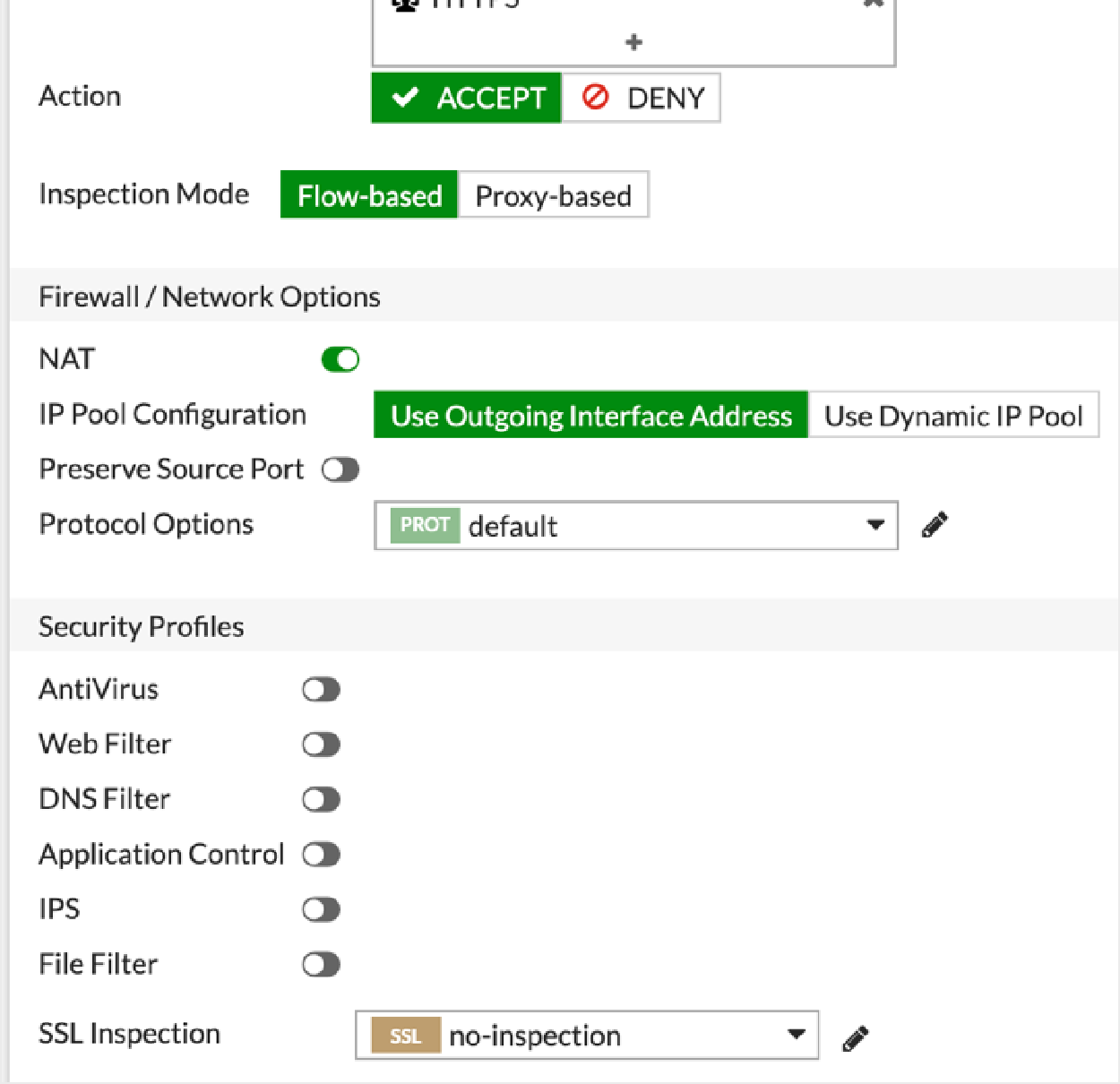
To create a route that pushes the VPN into RIB:
Go to Network > Static Routes.
Click + Create New and then OK.
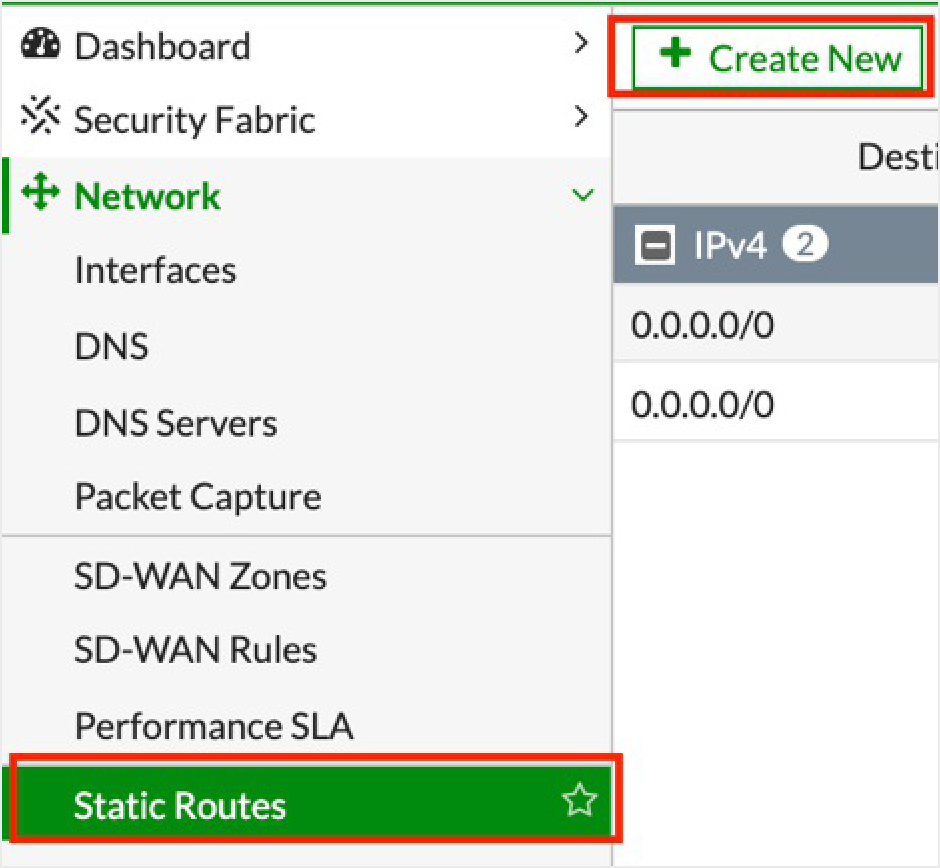
Ensure the Administrative Distance is the same as the original default route but with a higher Priority. For example:
config router static edit 3 set distance 5 set priority 10 set device "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" next endTo learn more about Administrative Distance and Priority: Fortinet documentation.
Enter the following commands and ensure there are two static routes installed:
get router info routing-table static Routing table for VRF=0 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [5/0] via 192.168.1.1, wan1 [5/0] is directly connected, NSKP-POP-Milan, [10/0]If both routes aren't displaying, your original default route might be obtained through DHCP. In the CLI, edit the original default route and
set dynamic-gateway enable, and add values for the following:config router static edit 2 set distance 5 set priority 5 set device "wan1" set dynamic-gateway enable next edit 3 set distance 5 set priority 10 set device "NSKP-POP-XXXXX" next endVerify your two static routes.
By default, policy-based routing (PBR) isn't enabled in the FortiGate GUI, so you must implement a policy-based router to redirect traffic to the Netskope proxy.
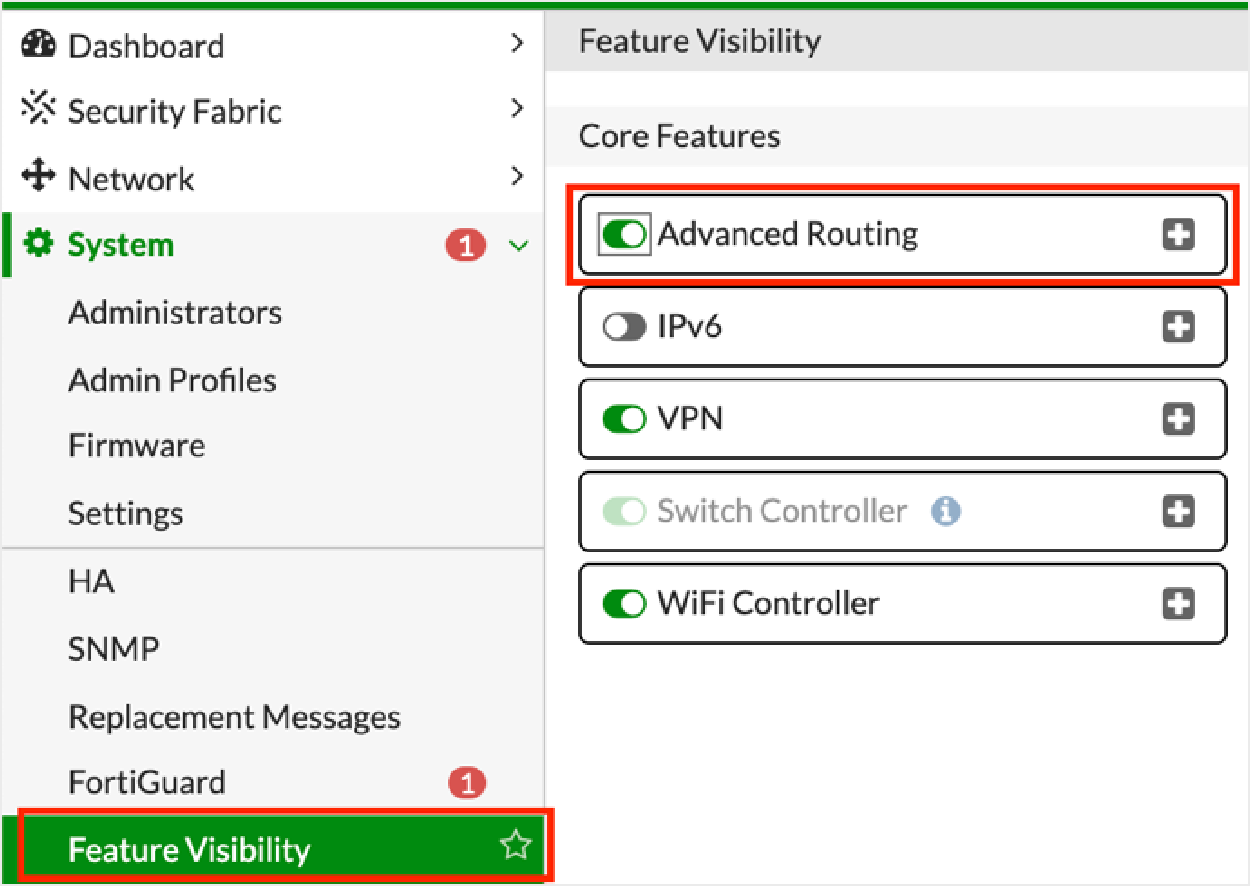
Go to System > Feature Visibility.
Under Core Features, enable Advanced Routing and click Apply. You don't need to reboot. This change doesn’t affect production.
Go to Network > Policy Routes.
Click + Create New.
Create at least two PBRs (one for HTTP and another for HTTPS).
To create the IPSec tunnels for FortiGate in the Netskope UI:
Go to Settings > Security Cloud Platform > IPSec.
Click Add New Tunnel.
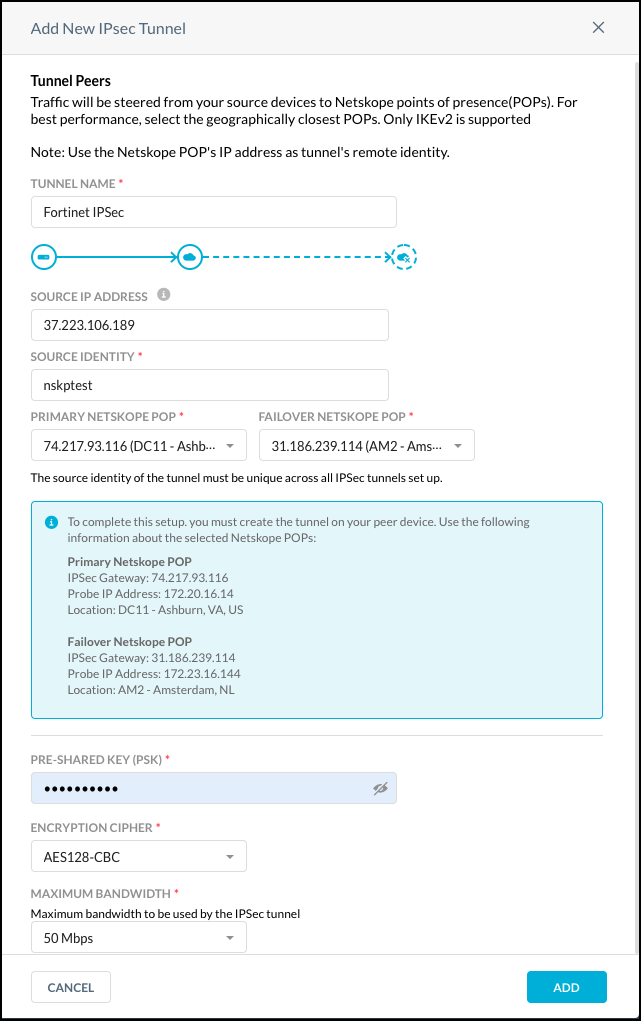
In the Add New IPSec Tunnel window:
Tunnel Name: Enter a name for the IPSec tunnel.
Source IP Address: (Optional) Enter the source peer IP address (i.e., exit public IP) of the FortiGate firewall that Netskope will receive packets from. Netskope identifies traffic belonging to your organization through your router or firewall IP addresses.
Source Identity: Enter an IP address, a fully-qualified domain name (FQDN), or an ID in email address format. For example, 1.1.1.1 or sourcelocation@company.com. The router or firewall uses the source identity for authentication during Internet Key Exchange (IKE).
Primary Netskope POP: Select the primary Netskope point of presence (POP) closest to you, and copy the IPSec Gateway IP address. You need this information to establish the primary IPSec tunnel on your FortiGate firewall. For optimal performance, Netskope recommends using the geographically closest POPs and configuring at least two tunnels for each egress location in your network.
Failover Netskope POP: Select the backup Netskope POP closest to you, and copy the IPSec Gateway IP address. You need this information to establish the backup IPSec tunnel on your FortiGate firewall. For optimal performance, Netskope recommends using the geographically closest POPs and configuring at least two tunnels for each egress location in your network.
Pre-Shared Key (PSK): Enter the pre-shared key that both sides of the tunnel will use to authenticate one another. The PSK must be unique for each tunnel.
Encryption Cipher: Select an encryption algorithm for the IPSec tunnel.
Maximum Bandwidth: Enter the maximum bandwidth for the IPSec tunnel. The tunnel size can be up to 1 Gbps. To enable the 1 Gbps option, contact your Sales Representative.
Advanced Settings: Click to view the following options.
Rekey: Select to rekey SAs when they expire. Netskope recommends using the default setting.
Reauthentication: Select to create new IKE and IPSec SAs when they expire. Netskope recommends using the default setting.
Trust X-Forwarded-For Header: Select to trust IP addresses contained in the X-Forwarded-For (XFF) HTTP header at the tunnel level. If you trust XFF at the tenant level, you can't select this option.
Apply to all traffic: Use the XFF HTTP header to identify all user traffic going through the IPSec tunnel.
Apply to specific NAT/proxy IP(s): Use the XFF HTTP header to identify traffic from specific NAT and proxy IP addresses going through the IPSec tunnel. Click +Add Another to add multiple IP addresses.
Click Add.
Following are some helpful commands for troubleshooting the configuration:
Enter the following command to enable debug for an IPSec connection:
diagnose debug application ike -1 diagnose debug enable
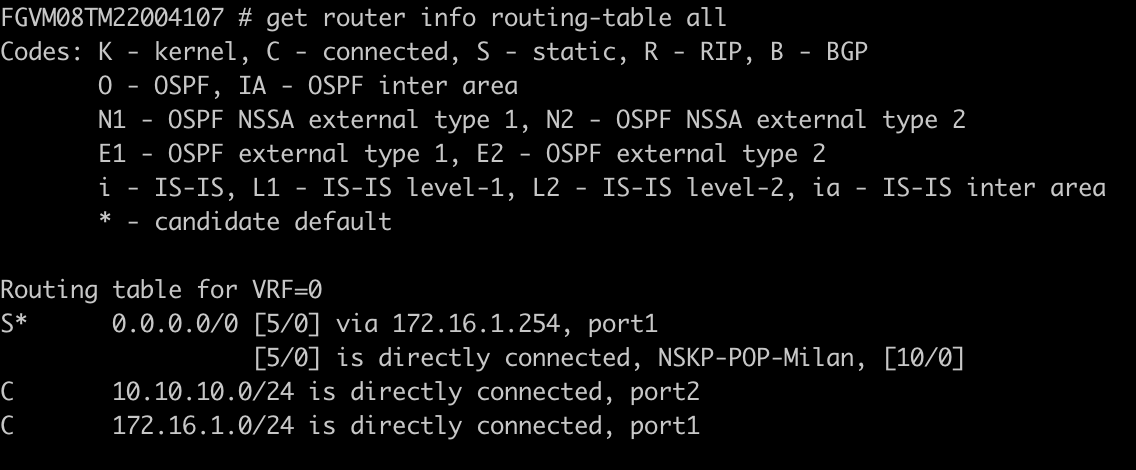
Enter the following command to obtain the whole routing table:
get router info routing-table all
Enter the following command to obtain an IPSec tunnel summary:
get vpn ipsec tunnel summary

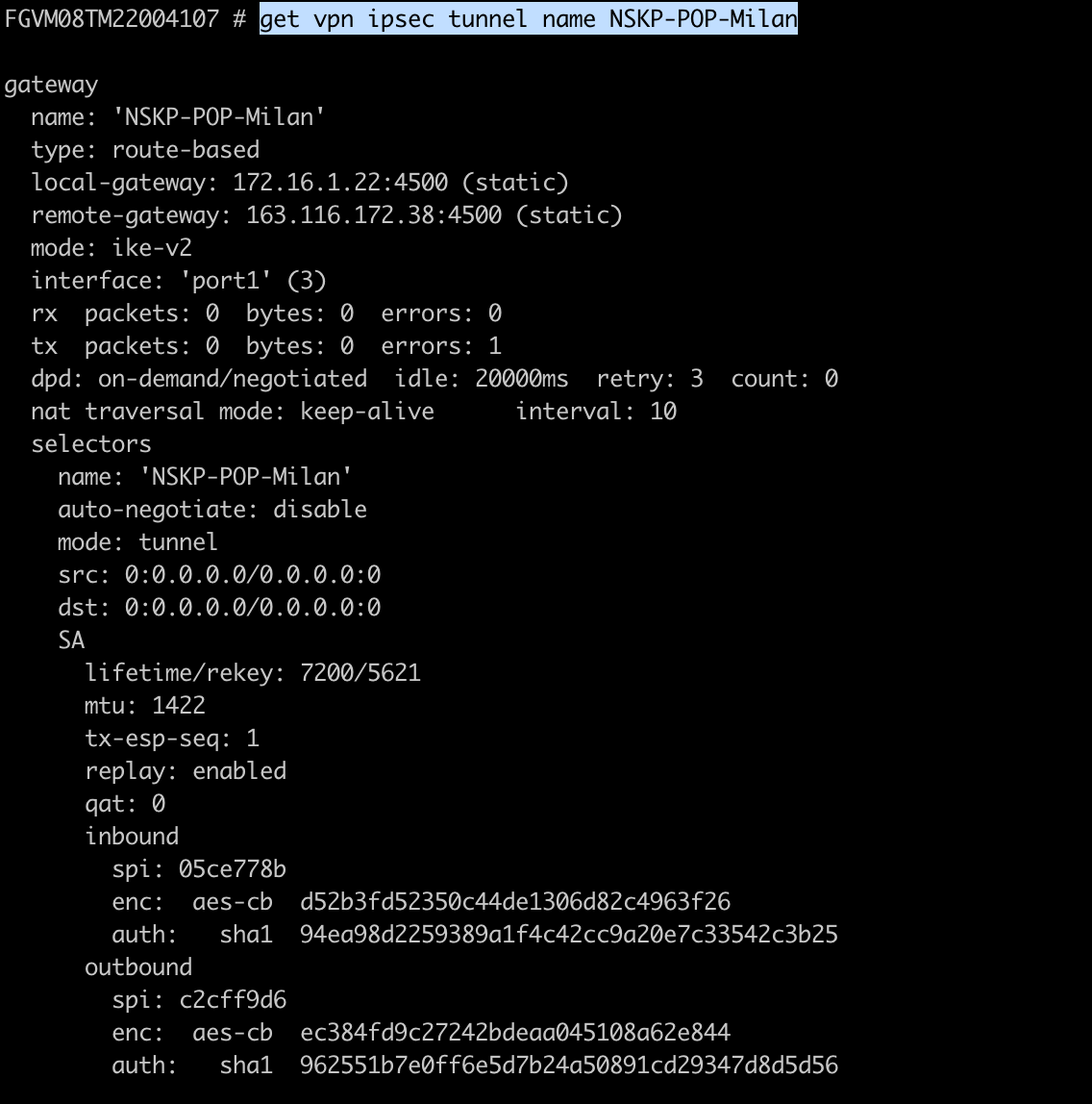
Enter the following command to obtain the IPSec tunnel details:
get vpn ipsec tunnel name NSKP-POP-XXXXXX