CrowdStrike Plugin for Threat Exchange
This document explains how to configure CrowdStrike with Threat Exchange in the Netskope Cloud Exchange platform. This integration allows for sharing of event driven intelligence that has been identified by CrowdStrike EDR or Netskope.
To complete this configuration, you need:
A Netskope tenant (or multiple; for example, production and development/test instances).
A Netskope Cloud Exchange tenant with the Threat Exchange module already configured.
A CrowdStrike Falcon Prevent account.
Create a custom File Profile.
Create a Malware Detection Profile.
Create a Real-time Protection Policy.
Create CrowdStrike API credentials.
Configure the CrowdStrike Plugin.
Configure sharing between Netskope and CrowdStrike.
Validate the CrowdStrike Plugin.
Click play to watch a video.
In the Netskope UI, go to Policies , select File , and click New File Profile.
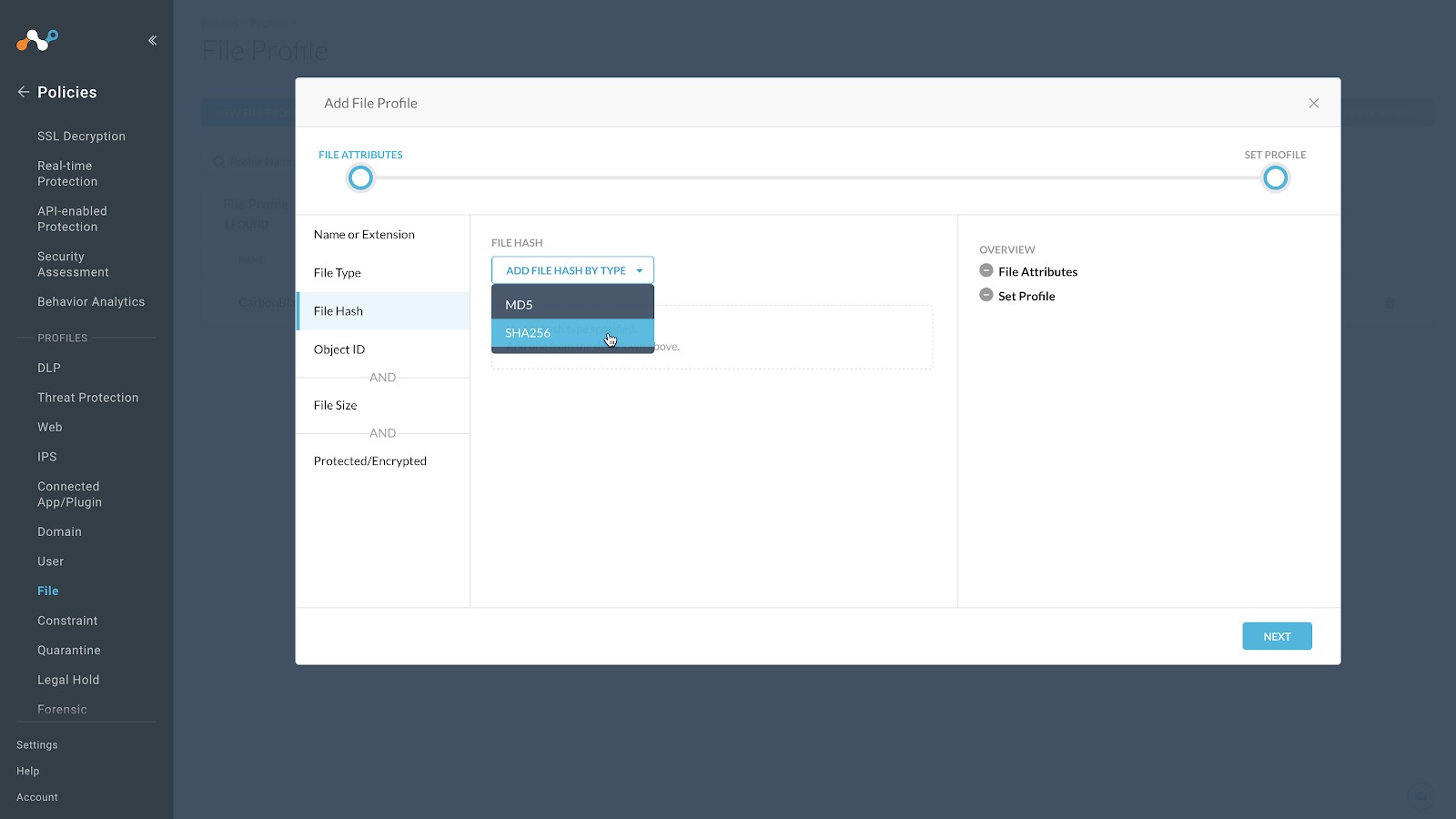
Click File Hash in the left panel, select SHA256 from the File Hash dropdown list.
Enter a temporary value in the text field. Netskope does not support progressing without having a value in this field, and recommends entering a string of 64 characters that consists of the character
f. For example,ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff. This will have a very low possibility of matching a valid file format.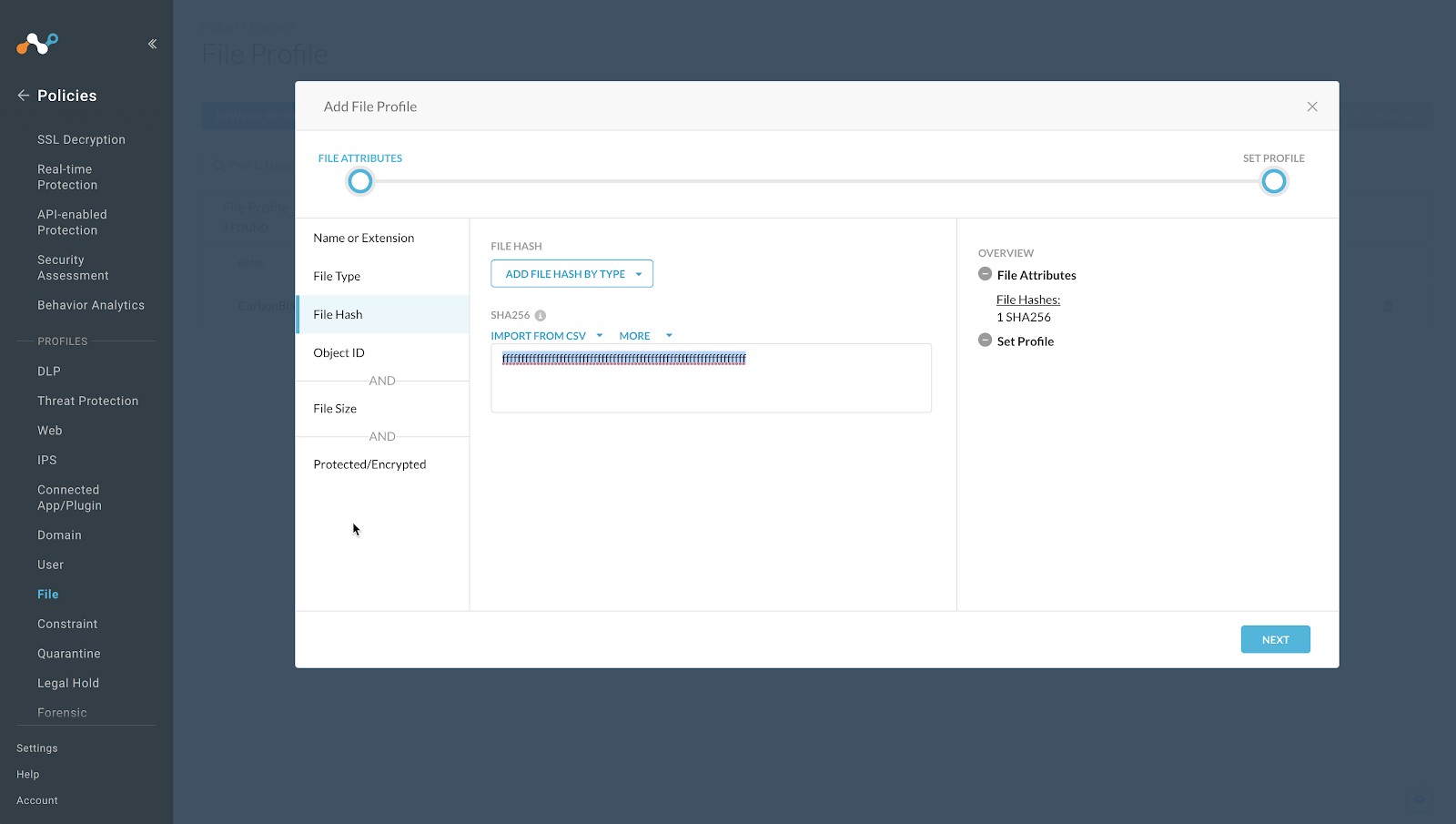
Click Next.
Enter a Profile Name and a Description. We recommend not having blank spaces in your profile name; use underscores for spaces.
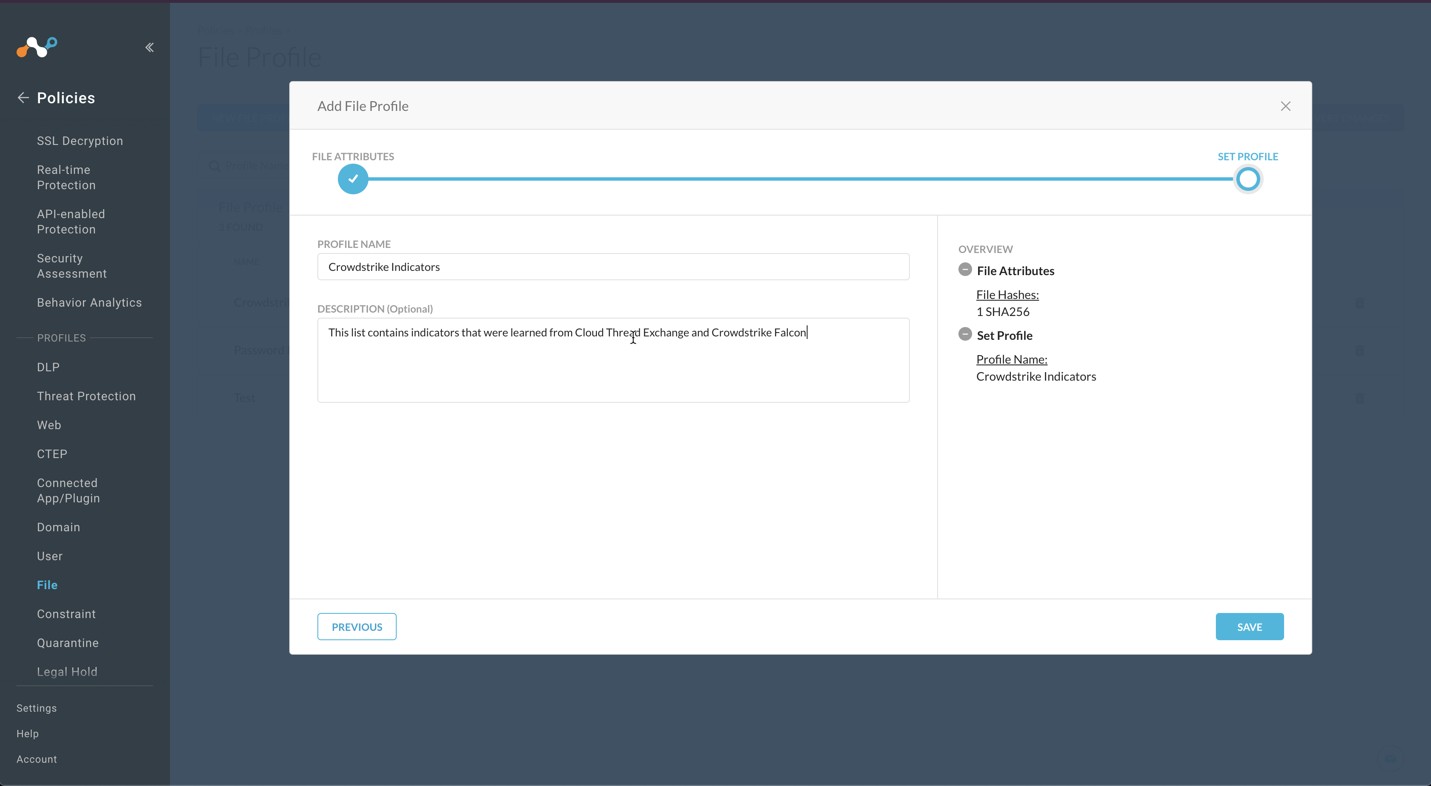
Click Save.
To publish this profile into the tenant, click Apply Changes in the top right.
In the Netskope UI, go to Policies, select Threat Protection , and click New Malware Detection Profile.
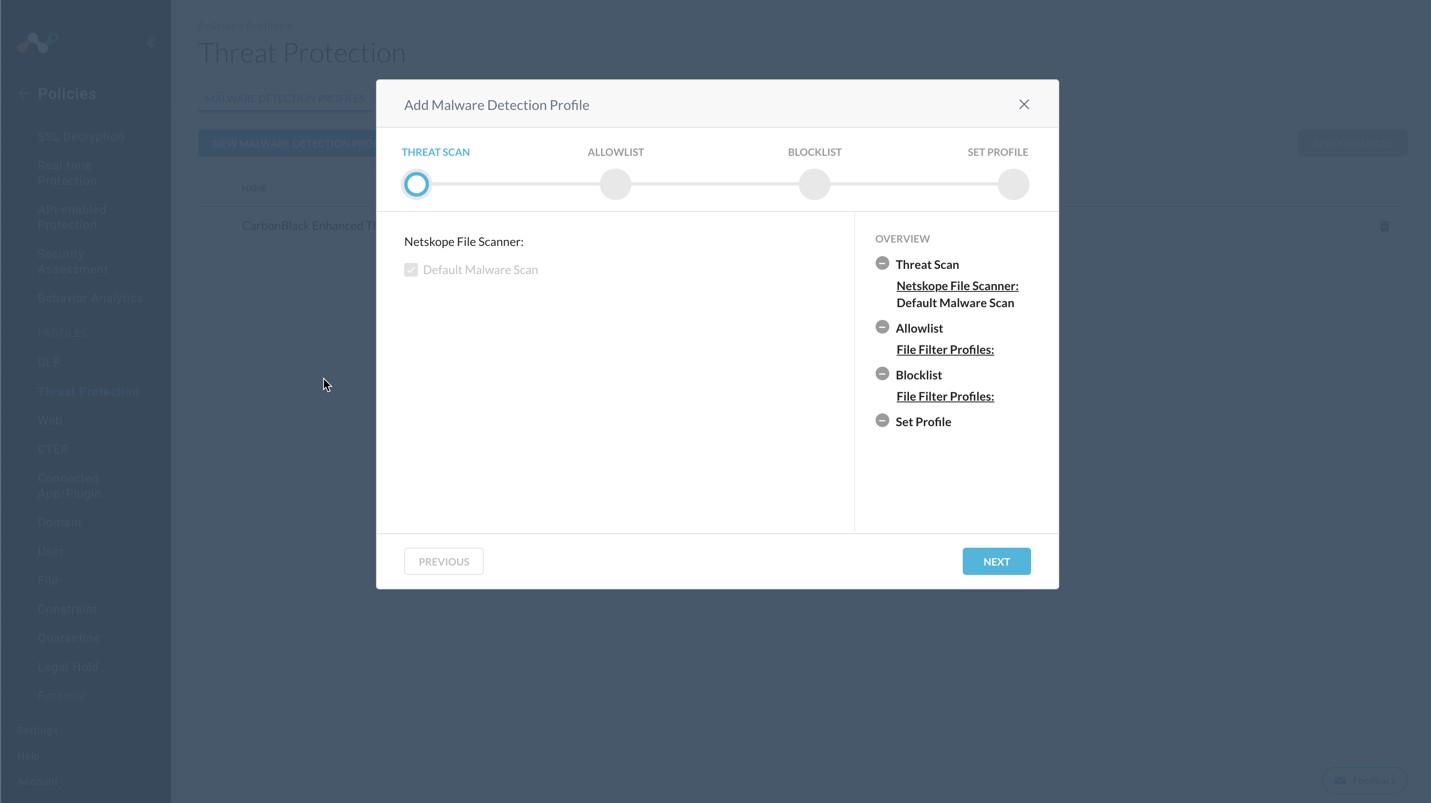
Click Next.
Note
For this configuration example, we will be using the intelligence for this list as a block list. Netskope does support inclusion of both allow and block lists in the threat profiles.
Click Next again.
Select the File Profile you created in the previous section and click Next.
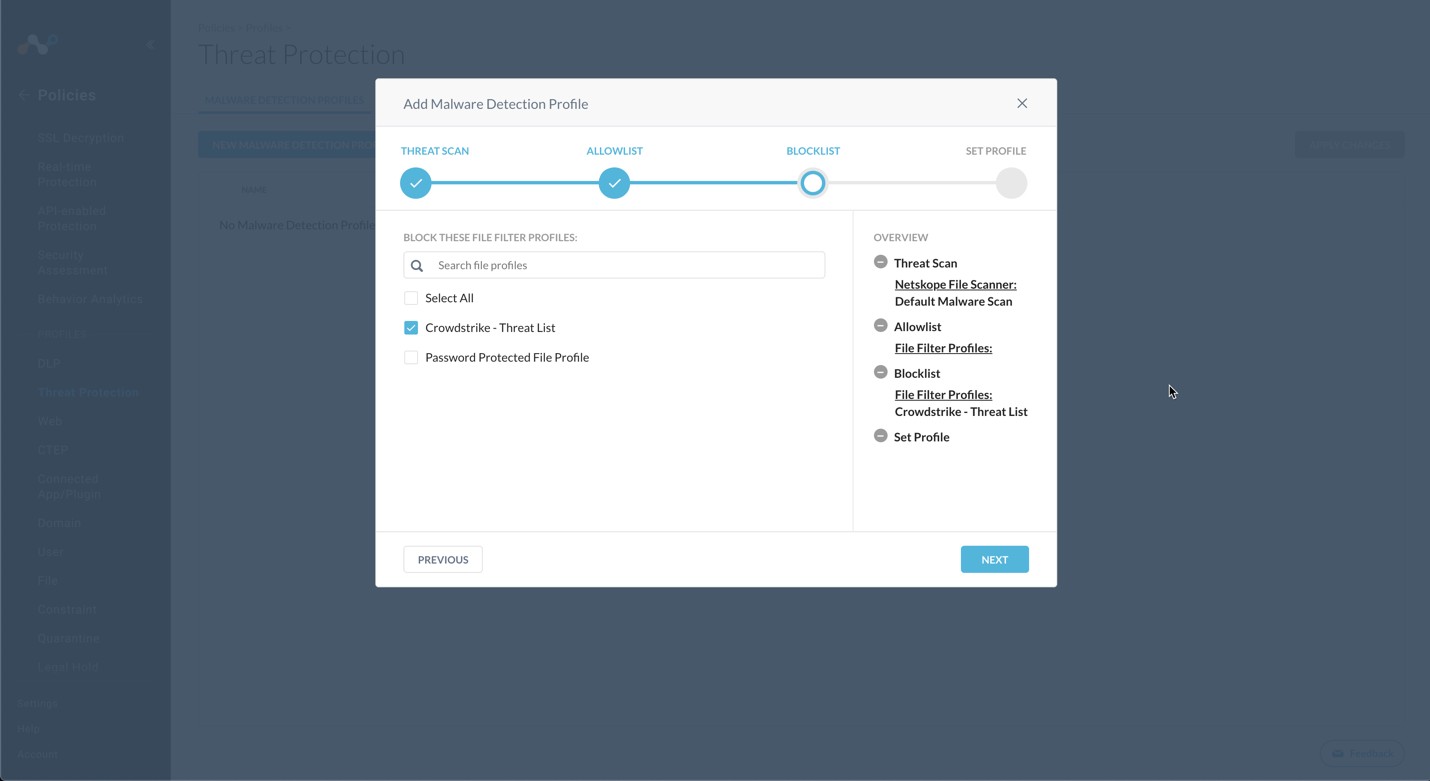
Enter a Malware Detection Profile name and click Save Malware Detection Profile.
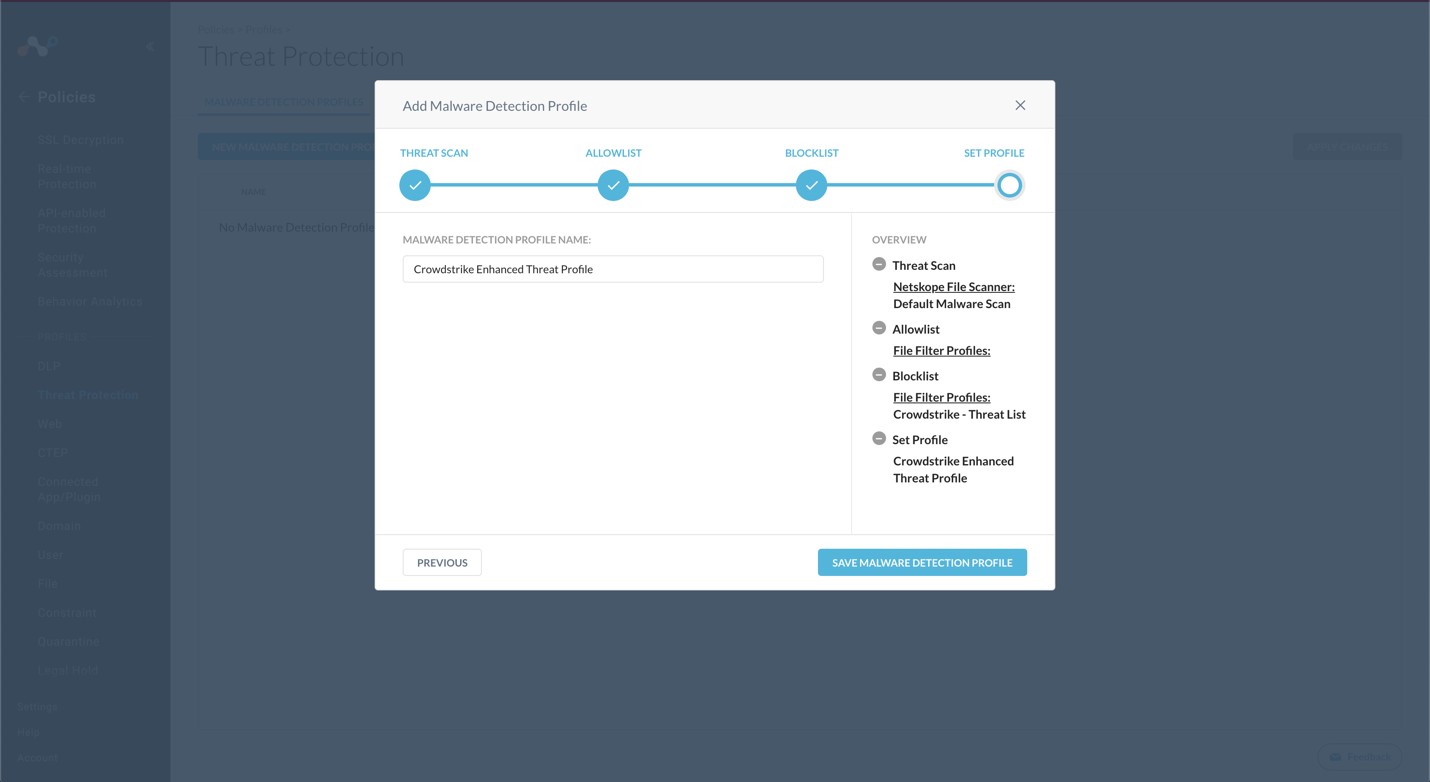
To publish this profile in the tenant, click Apply Changes in the top right.
These instructions apply to the new Real-time Protection policy workflow.
In the Netskope UI, go to Policies > Real-time Protection.
Note
The policy configured here is just an example. Modify as appropriate for your organization.
Click New Policy and select Threat Protection.
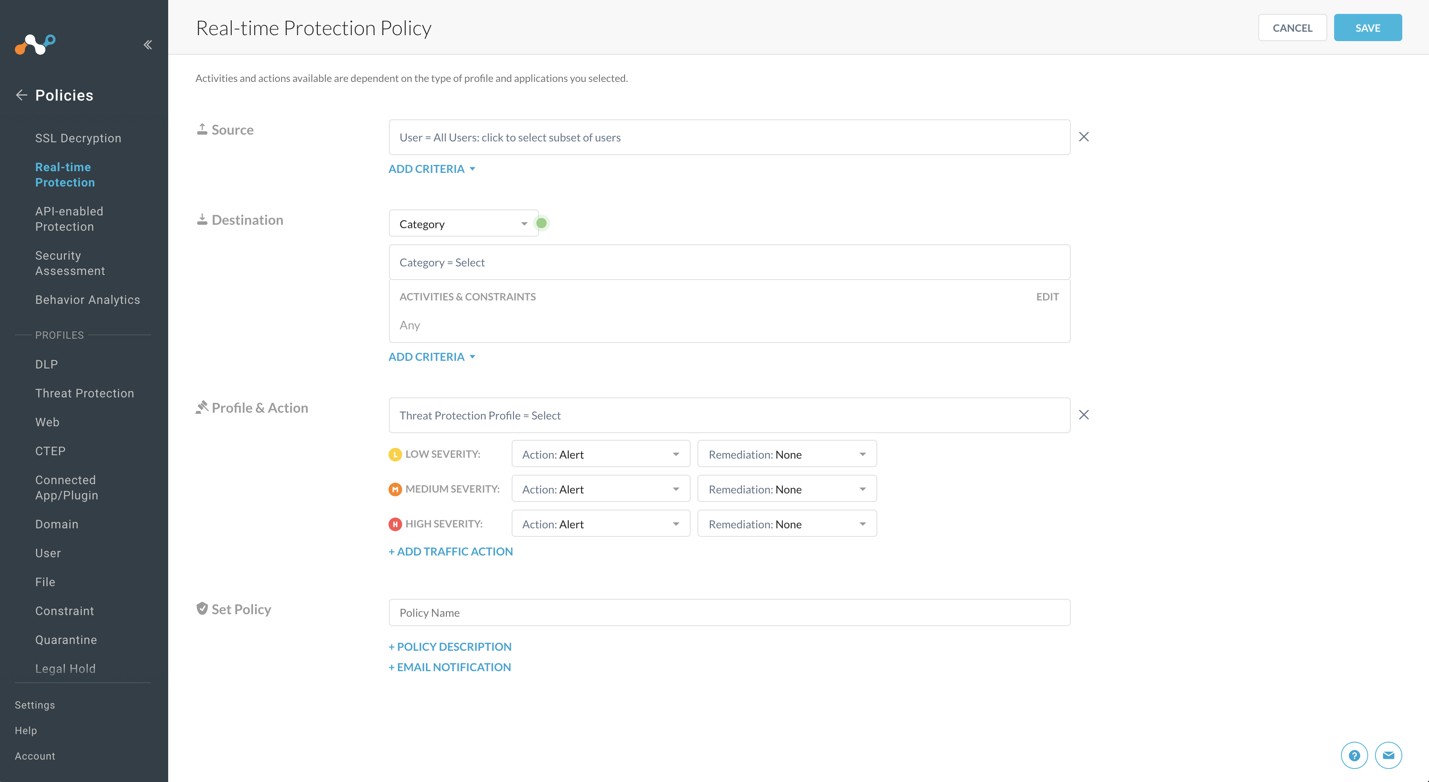
For Source, leave the default (User = All Users)
For Destination: select Category
The Category section expands and allows you to search and select categories. Click Select All.
When finished, click outside of the Category section.
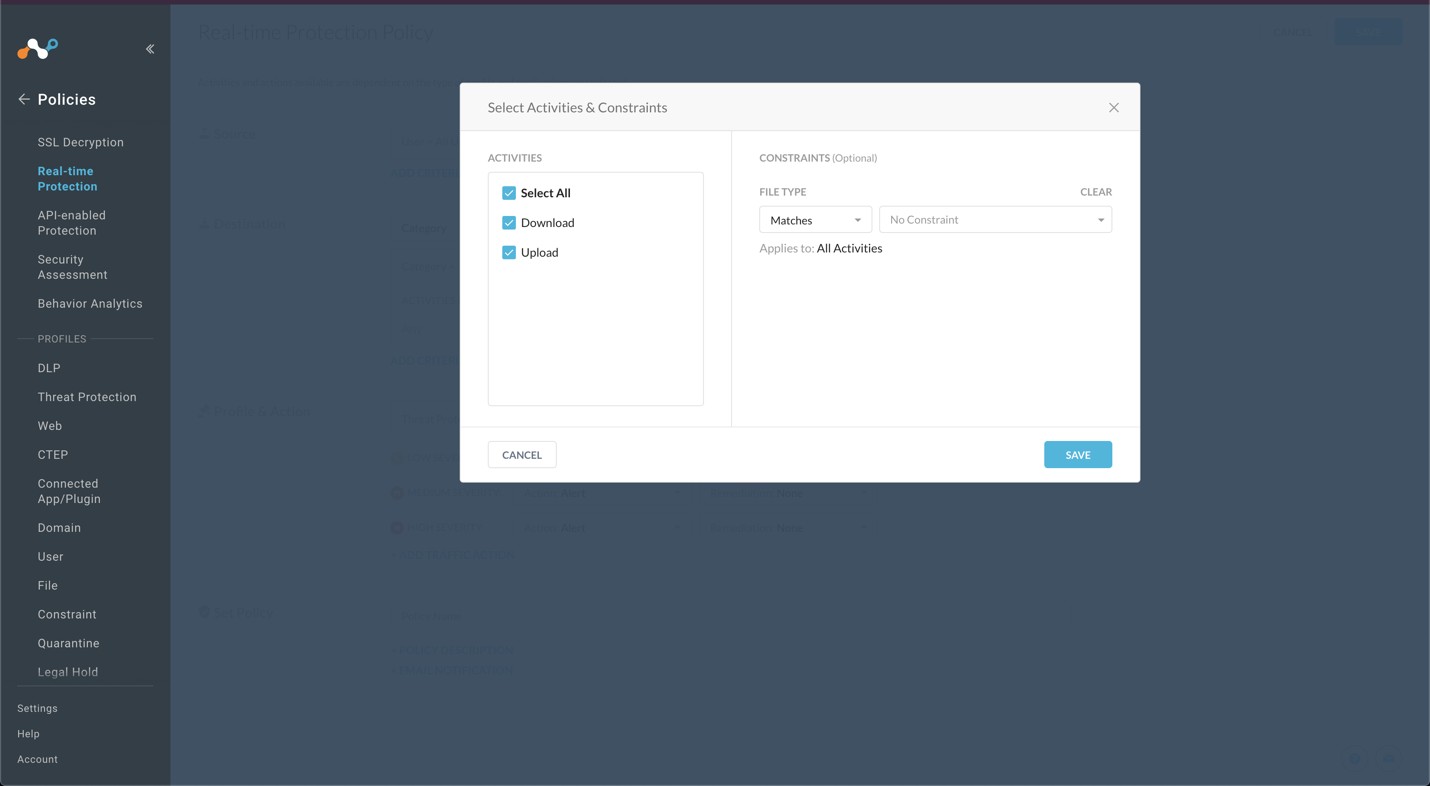
When the Activities & Constraints section opens, click Edit.
Select Upload and Download, and then click Save.
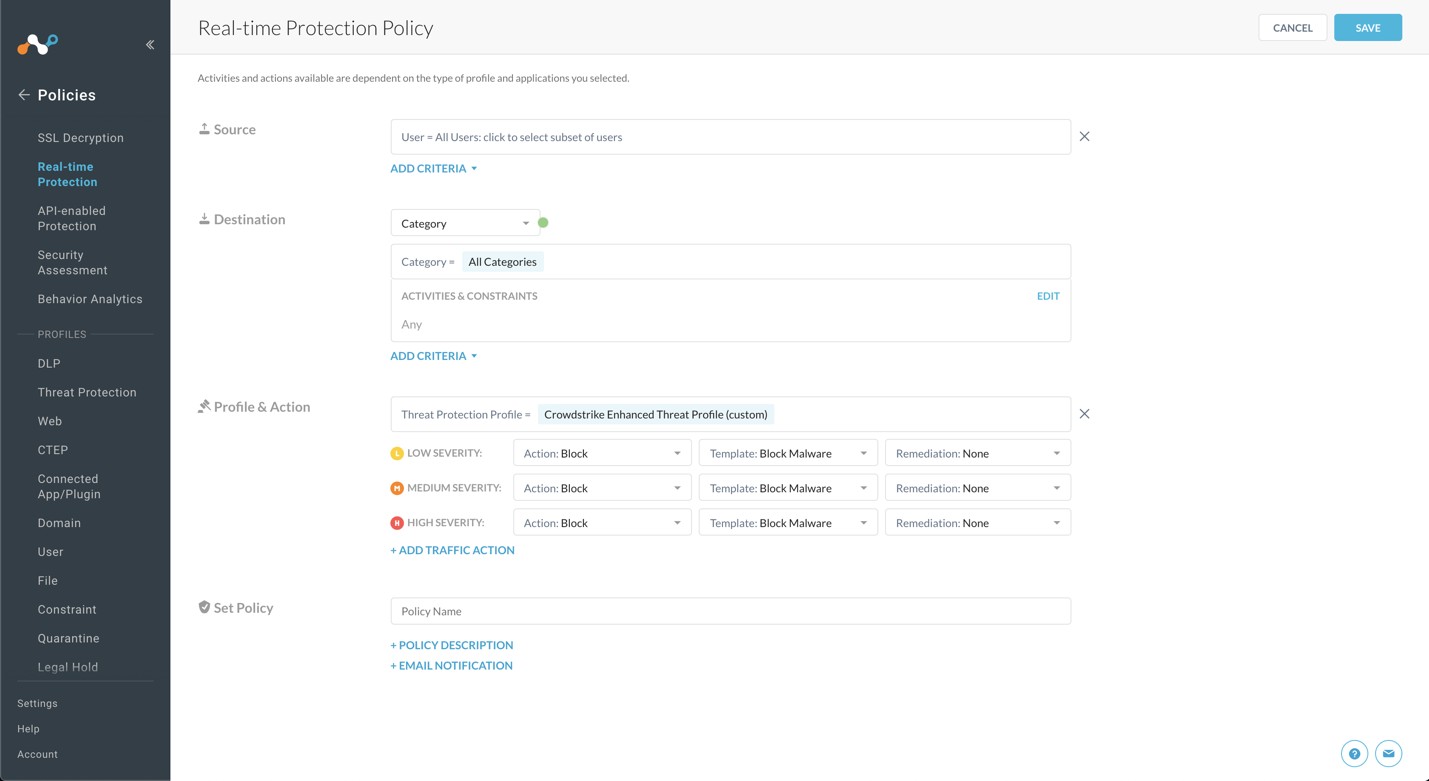
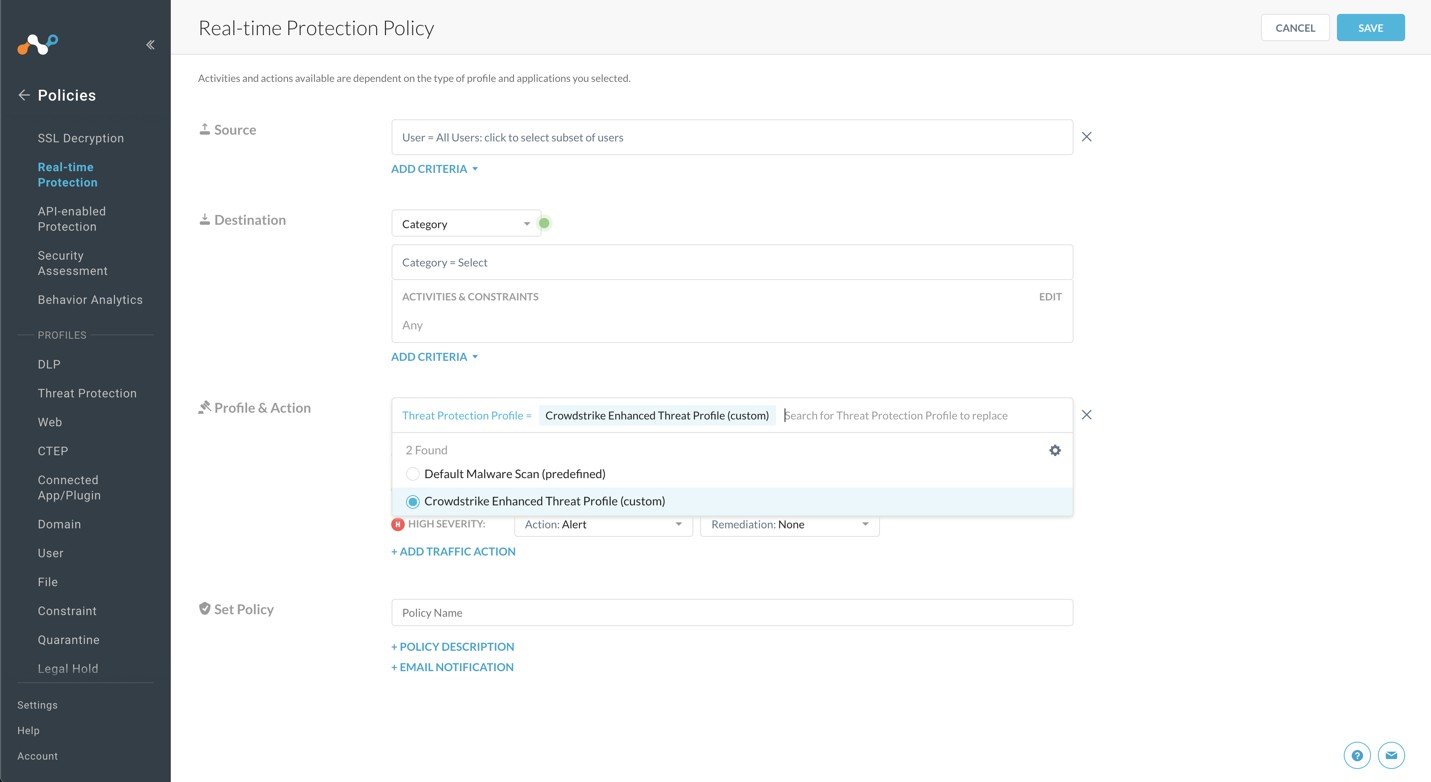
For Profile & Action, click in the text field.
Select the Malware Detection profile you created in the previous section.
For the Severity Levels, change all of the Actions settings from
Action: AlerttoAction: Block.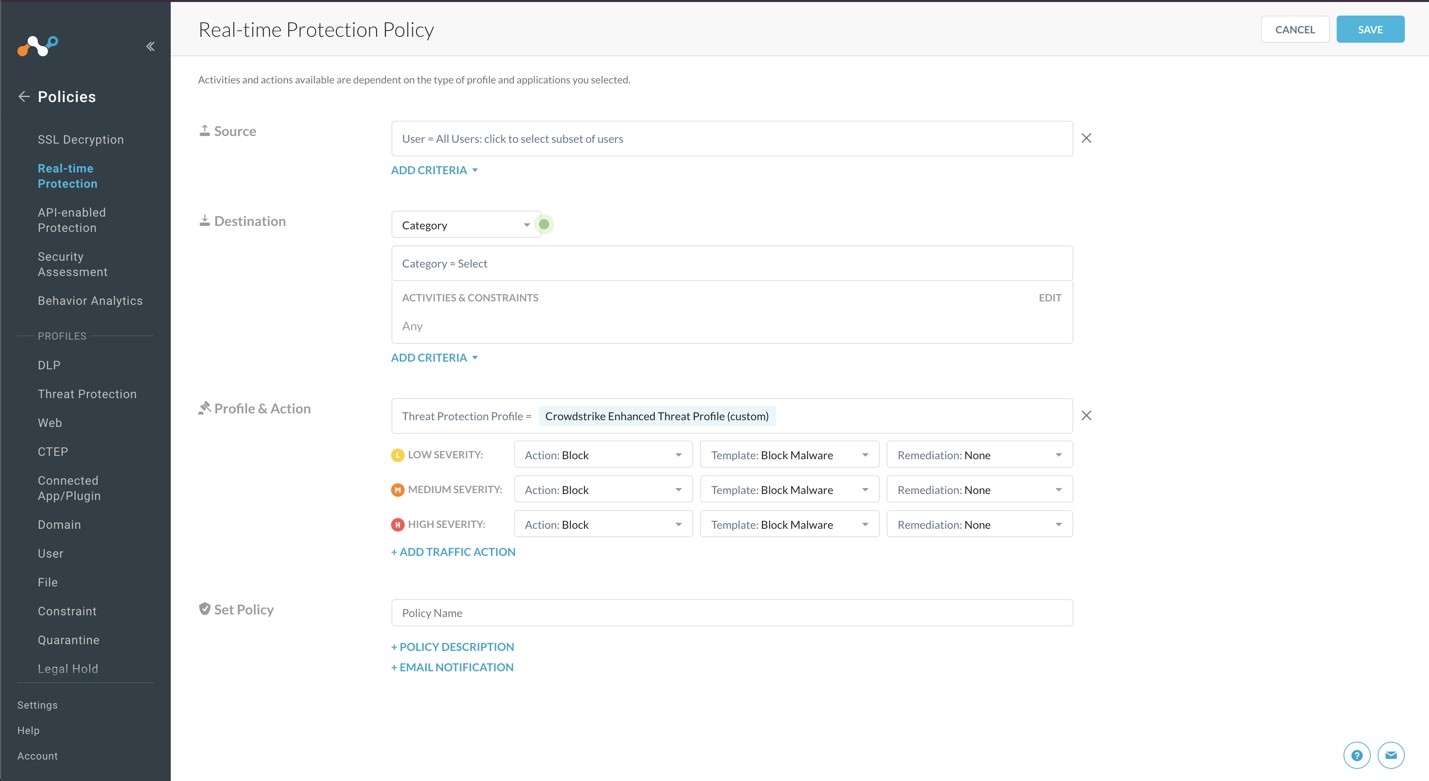
Select a template to choose which block message is sent to the user.
For Set Policy, enter a descriptive Policy Name.
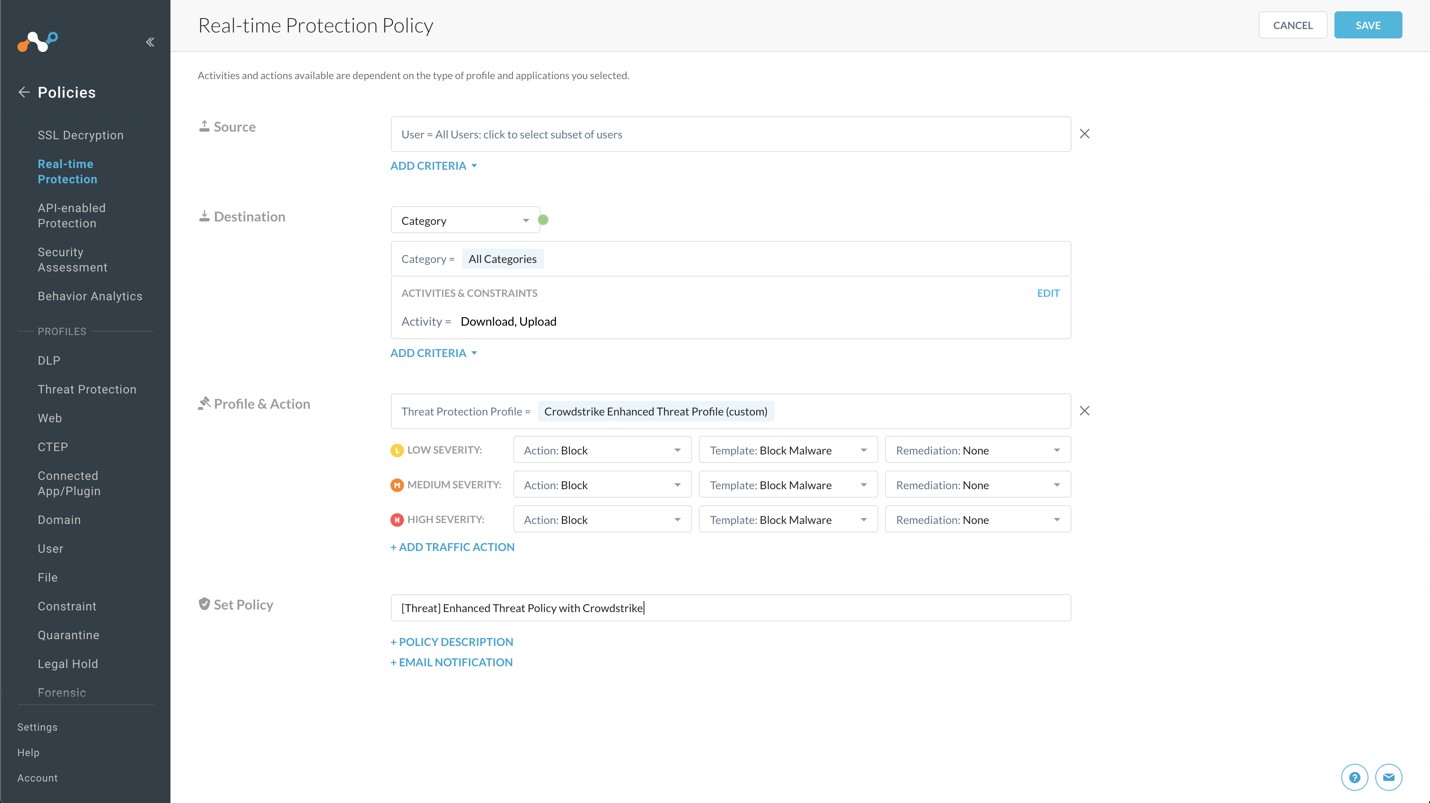
Click Save in the top right to save the policy.
Choose the To the top option when it appear. (Or appropriate location in your security policy)
To publish this policy into the tenant, select Apply Changes in the top right.
Log in to your Falcon Console.
Go to the Dashboard, click the Falcon icon, and then Support. Click API Client and Keys.
Click Add new API client.
Enter a Client Name.
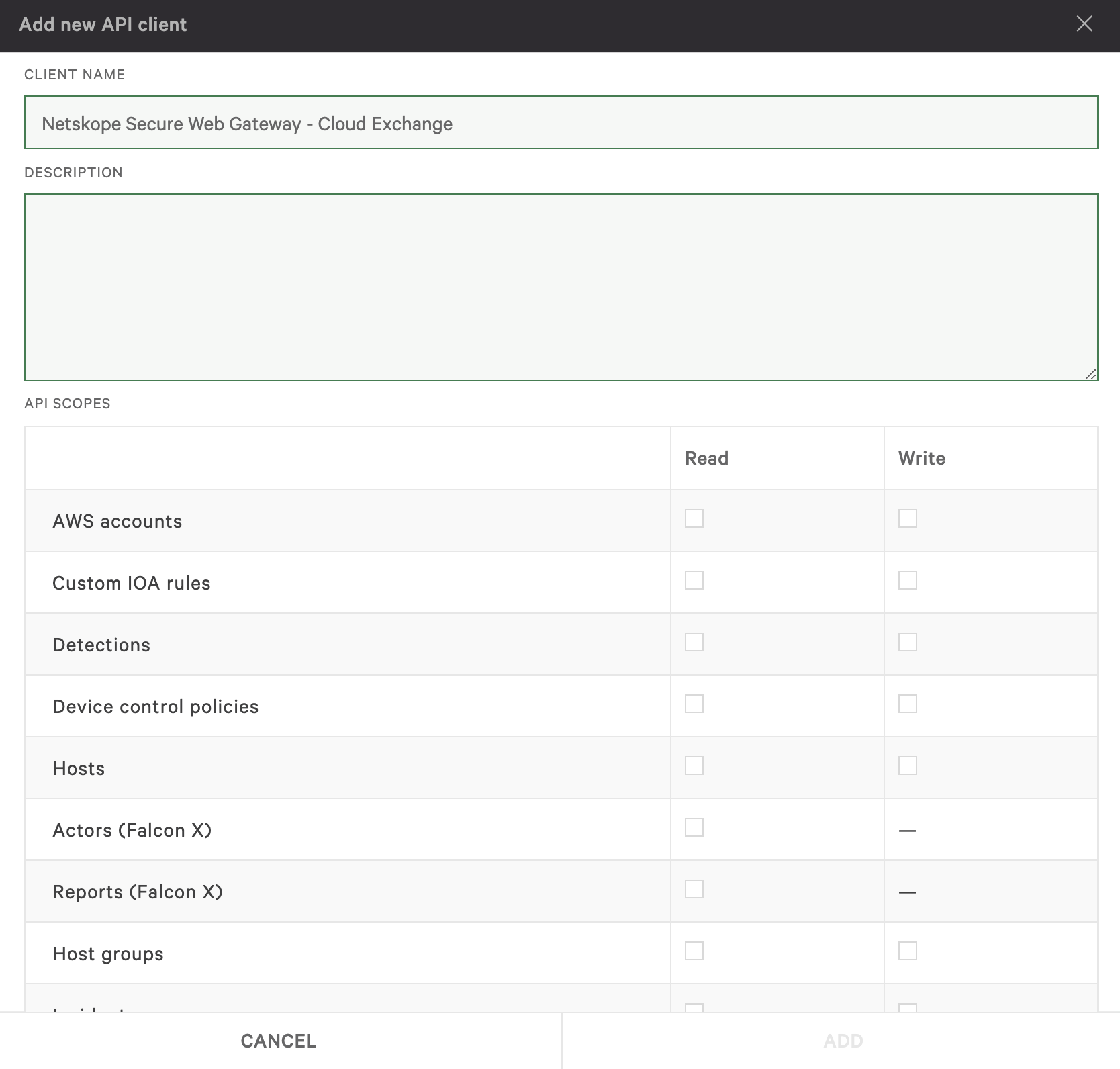
Configure these API scopes:
Detections = Read
Incidents = Read
IoC Manager APIs = Read/Write
IoCs (Indicators of Compromise) = Read/Write
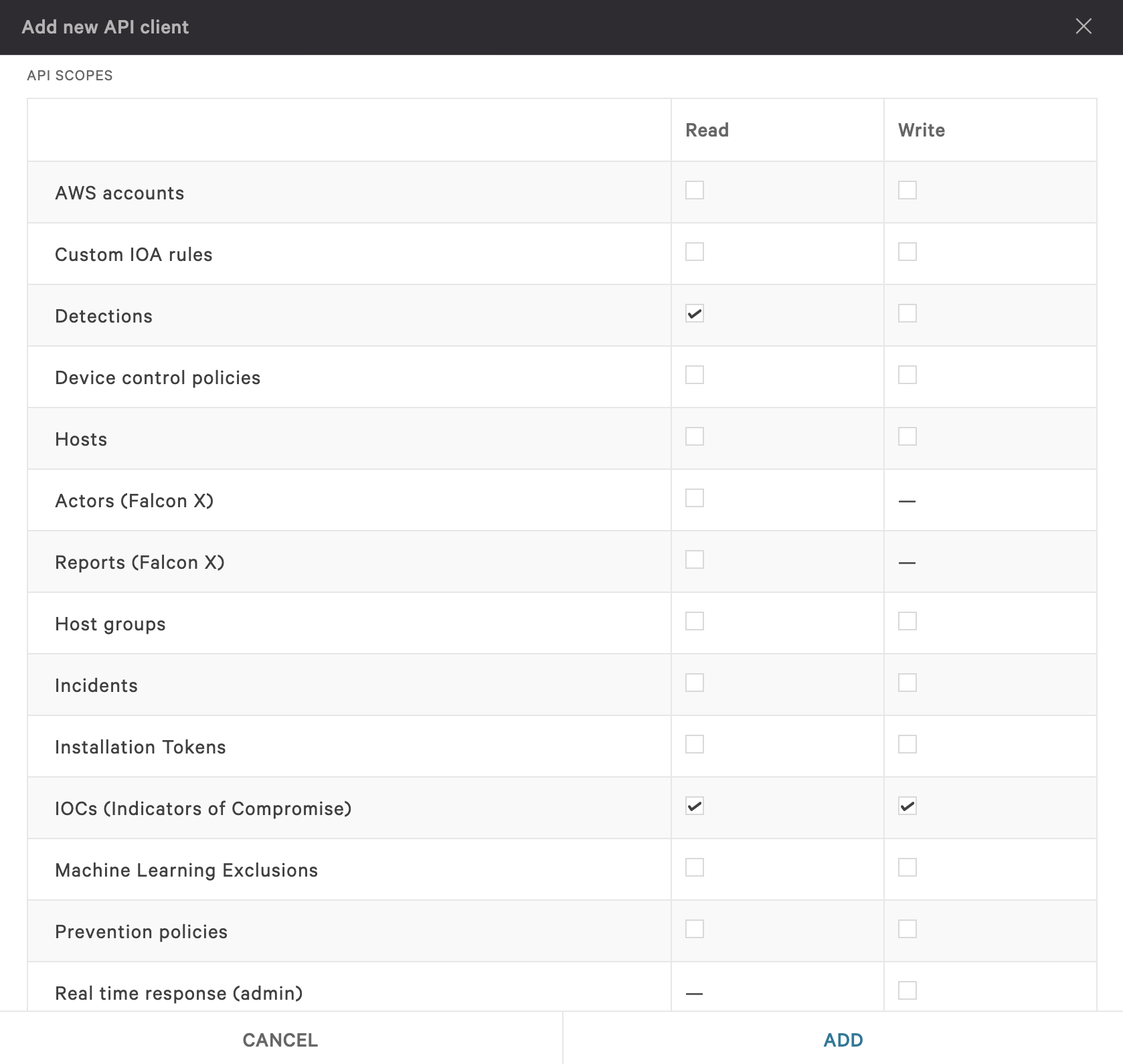
When finished, click Add.
Copy the data on the next screen. You will need the Client ID, Client Secret, and Base URL when you configure the CrowdStrike plugin for Threat Exchange.
Important
You will only see the secret on this dialog, if you did not copy it, you will need to regenerate it.
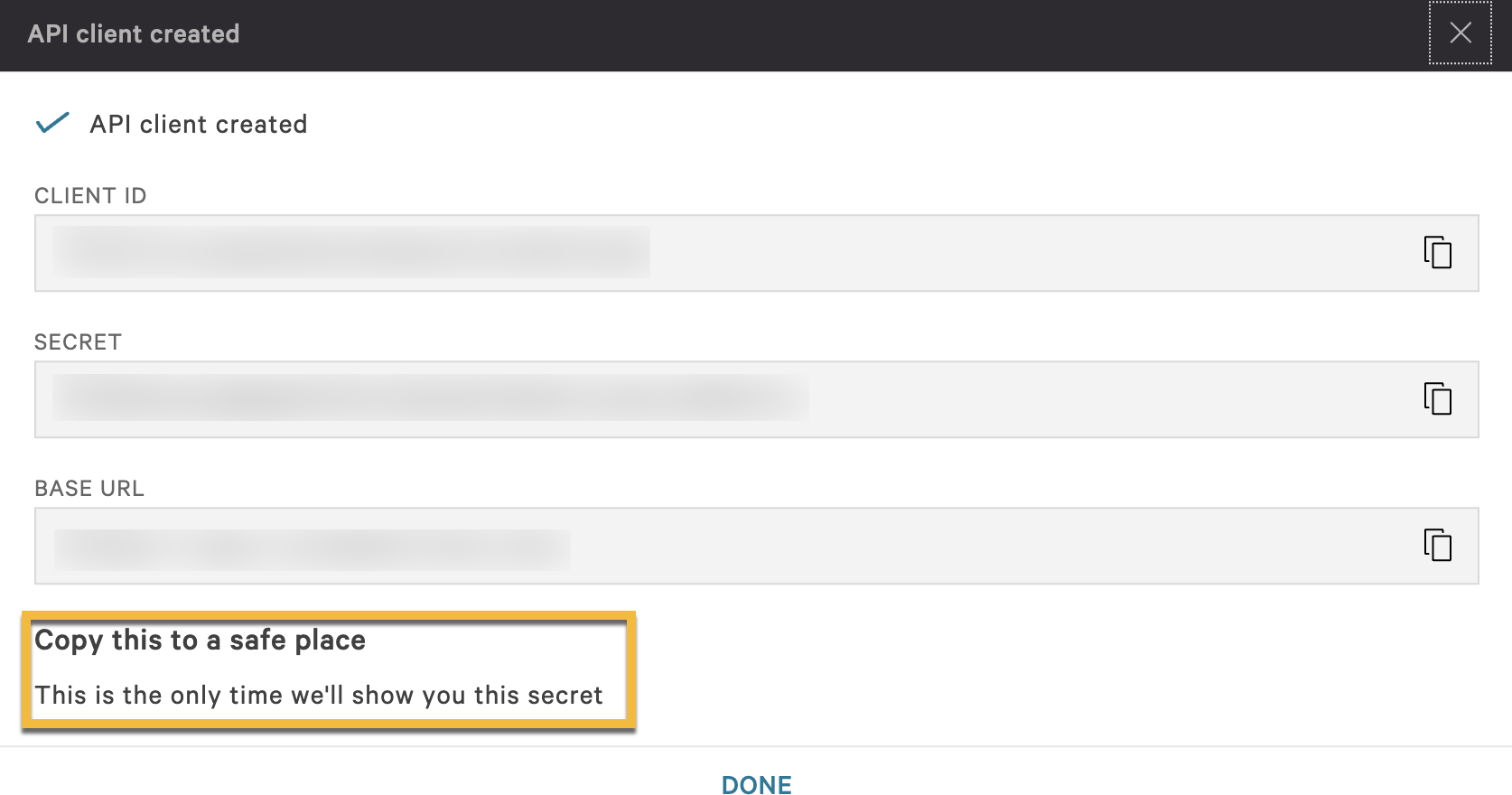
You will need the CrowdStrike API Client Base URL, Client ID, and Client Secret to complete this configuration.
In Cloud Exchange, go to Settings and click Plugins.
Search for and select the CrowdStrike box to open the plugin creation pages.
Enter and select the Basic Information on the first page:
Configuration Name: Enter a name appropriate for your integration.
Filter Query: Leave the default.
Age of Indicators: Leave the default.
Poll Interval: Adjust to environment needs. We recommend not to go below 5 minutes for production environments.
Aging Criteria: Leave the default.
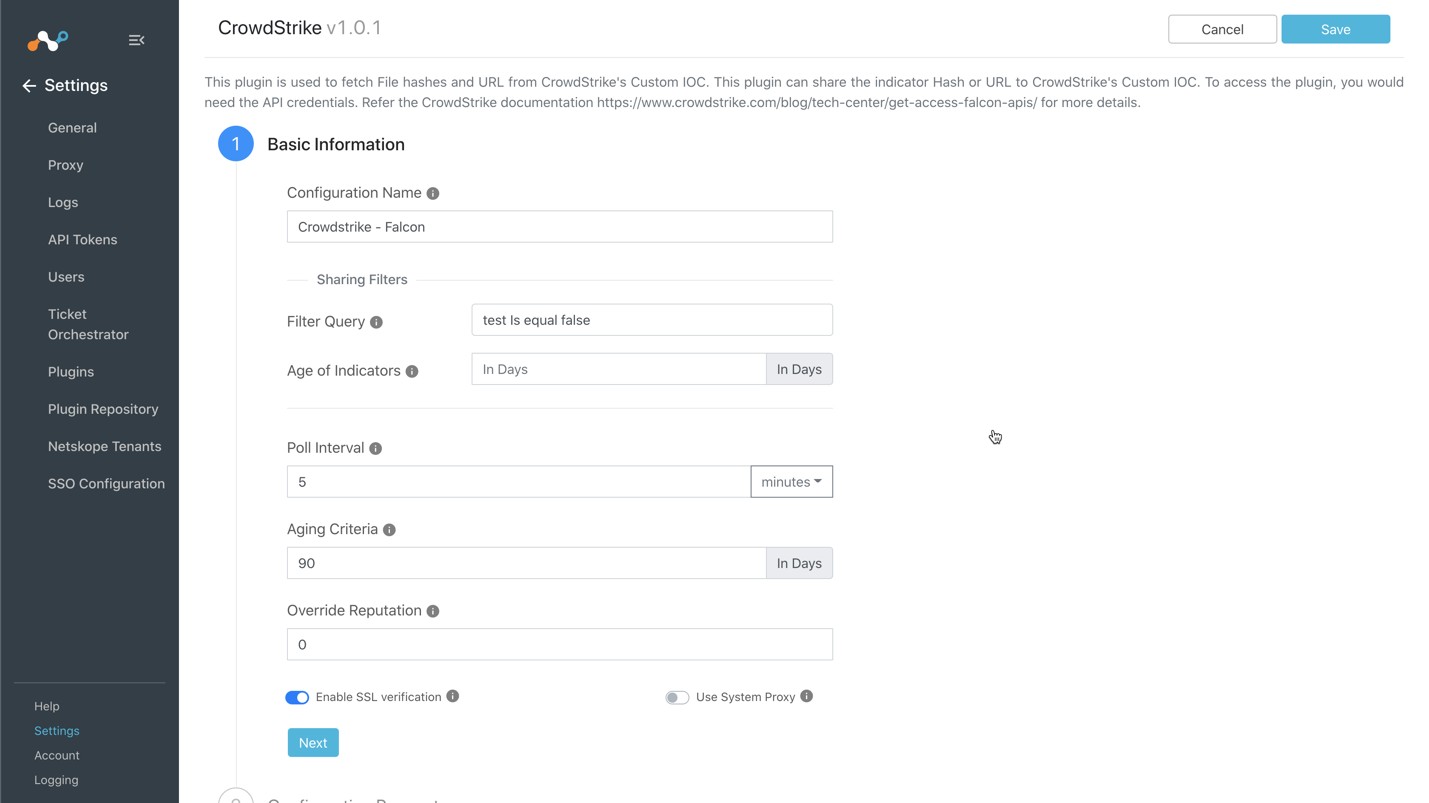
Click Next.
Enter and select the Configuration Parameters on the second page:
Base URL: From the CrowdStrike API Client you created previously. Should be the default for most use cases.
Client ID: From the CrowdStrike API Client you created previously.
Client Secret: From the CrowdStrike API Client you created previously.
Enable Polling: Leave the default.
Type of Threat data to pull: Select Malware.
Initial Range: Set an appropriate for your use case. The default is 7 days of past detections.
Indicator Batch Size: Leave the default.
CrowdStrike Share Level: Leave the default.
CrowdStrike Detect Policy: Leave the default.
IoC Source: Adjust appropriately. The default works for most scenarios.
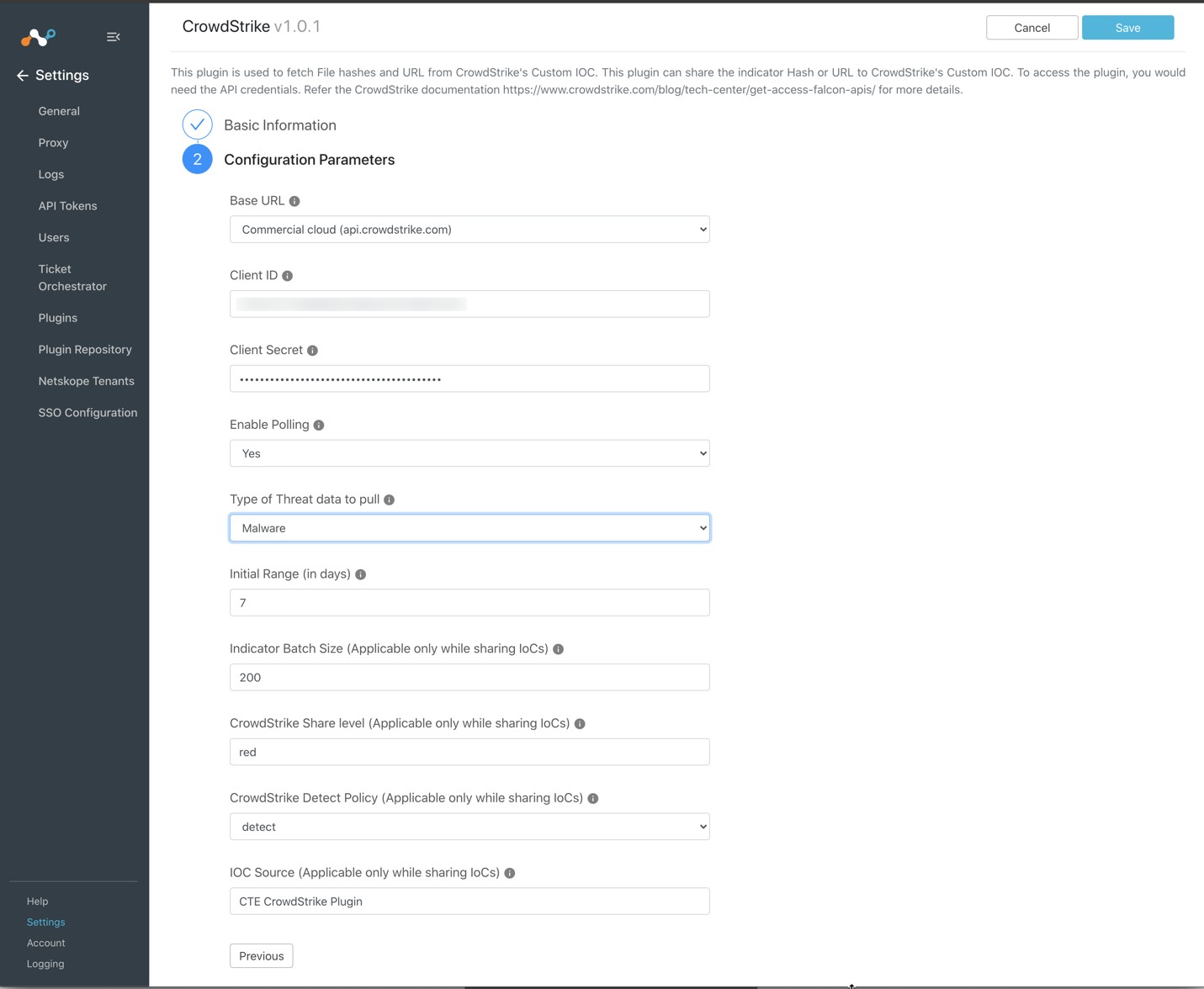
Click Save in the top right. Go to Threat Exchange > Plugins to see your new CrowdStrike plugin.
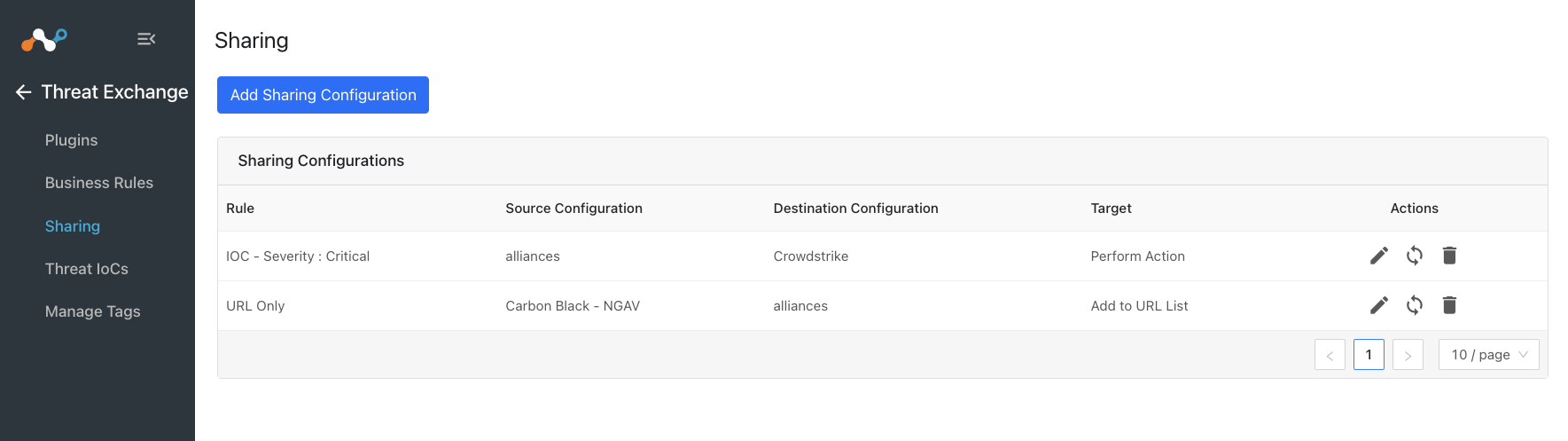
Go to Threat Exchange and select Sharing. The Sharing page displays the existing relationships for each sharing configuration in grid view as shown below. The Sharing page also has inputs to configure new sharing from one plugin to another.
Click Add Sharing Configuration, and in the Source Configuration dropdown list, select CrowdStrike.
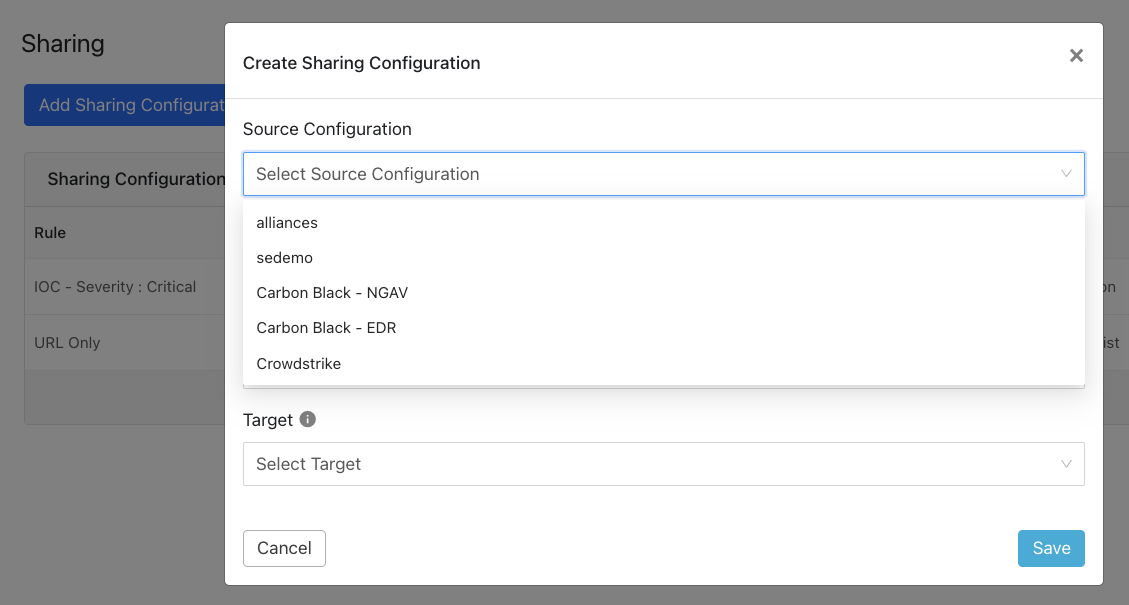
Select a Business Rule, and then select Netskope for the Destination Configuration. Sharing configurations are unidirectional. data obtained from one plugin is shared with another plugin. To achieve bi- or multi-directional sharing, configure each separately.
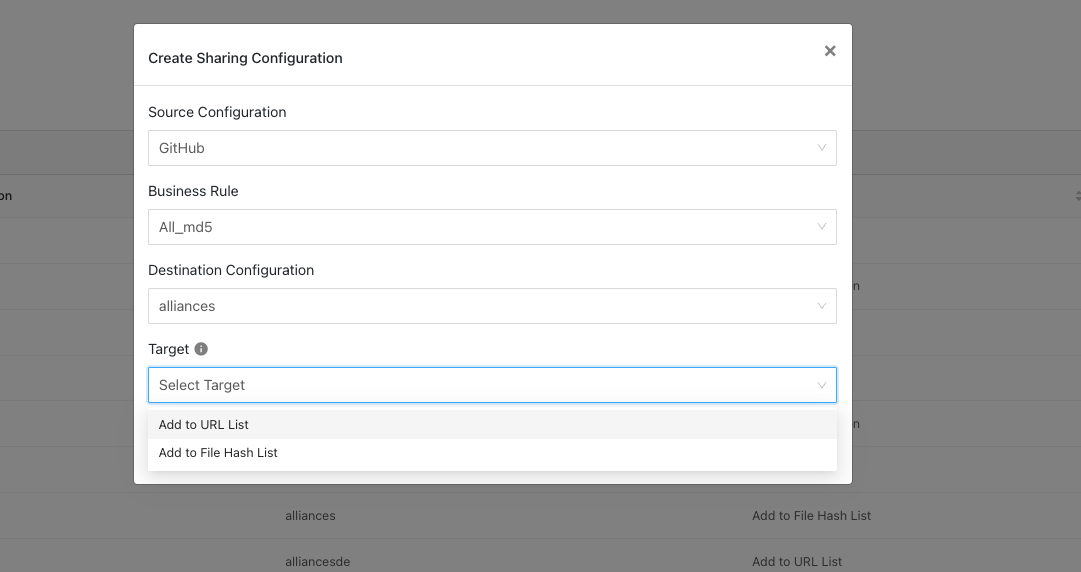
Select a Target. Each plugin will have a different target or destination for the IoC.
Click Save.
Repeat steps 2-5, but select Netskope as the Source Configuration and CrowdStrike as the Destination Configuration.
Click Save.
Adding a new sharing configuration on the active source poll will share the existing IoCs of the source configuration to the destination configuration. Whenever a new sharing configuration is built, all the active IoCs will also be considered for sharing if they match the source/destination combination.
Note
Plugins that do not have API for ingesting data cannot receive threat data. This is true of the installed plugin API Source, which provides a bucket associated with an API endpoint for remote 3rd-party systems to push data to. Once a Sharing policy has been added, it takes effect.
After a sharing configuration has been created, the sharing table will show the rule being invoked, the source system providing the potential IoC matches, the destination system that will receive matching IoC, and the target applicable to that rule. Multiple Sharing configurations can be made to support mapping certain IoC to multiple targets even on the system destination system.
Modify, Test, or Delete a Sharing Configuration
Each configuration supports 3 actions:
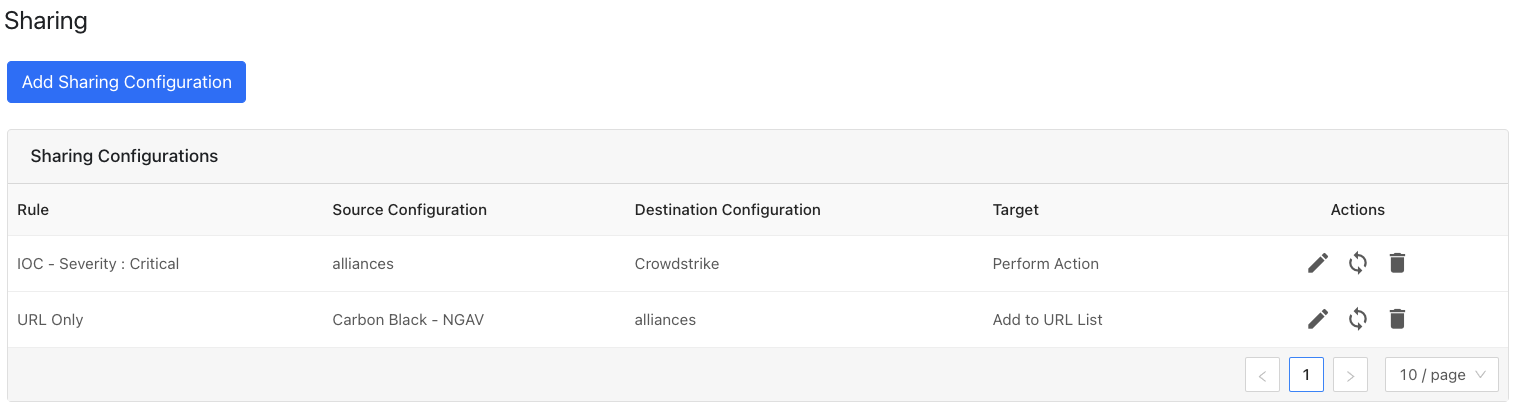 |
Edit the rule by clicking on the pencil icon.
Test the rule by clicking on the synchronization icon. This tests how many IoC will actually be sent to the destination system based on the timeframe and the rule.
Delete the rule by clicking on the garbage can icon.
In order to validate the workflow, you must have Netskope Alerts and/or CrowdStrike Detections. These will be queried based on the polling interval previously configured in the plugins.
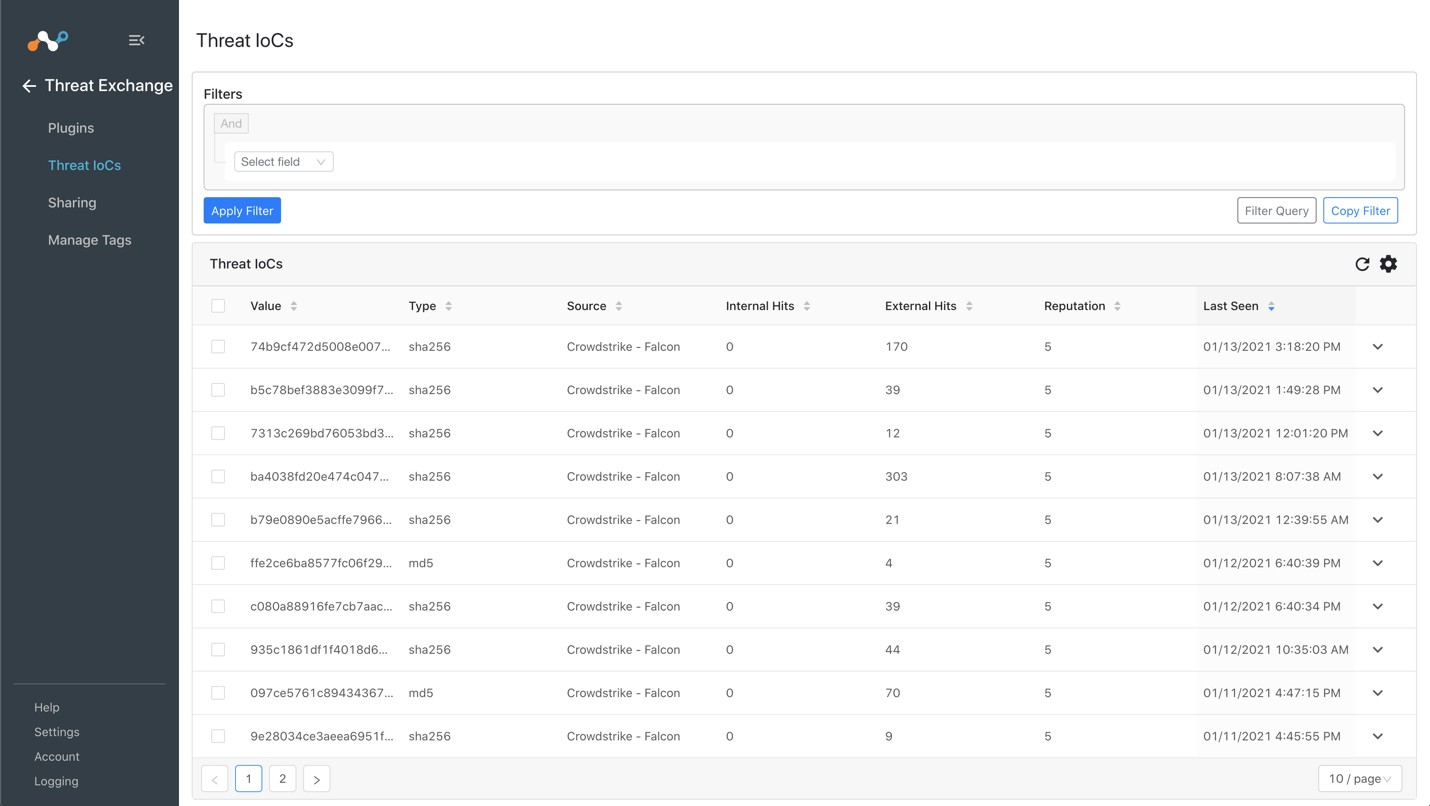
Go to Threat Exchange and select Threat IoCs.
You should see records from your CrowdStrike plugin. You can filter based on Source values to check both the Netskope and CrowdStrike plugins.
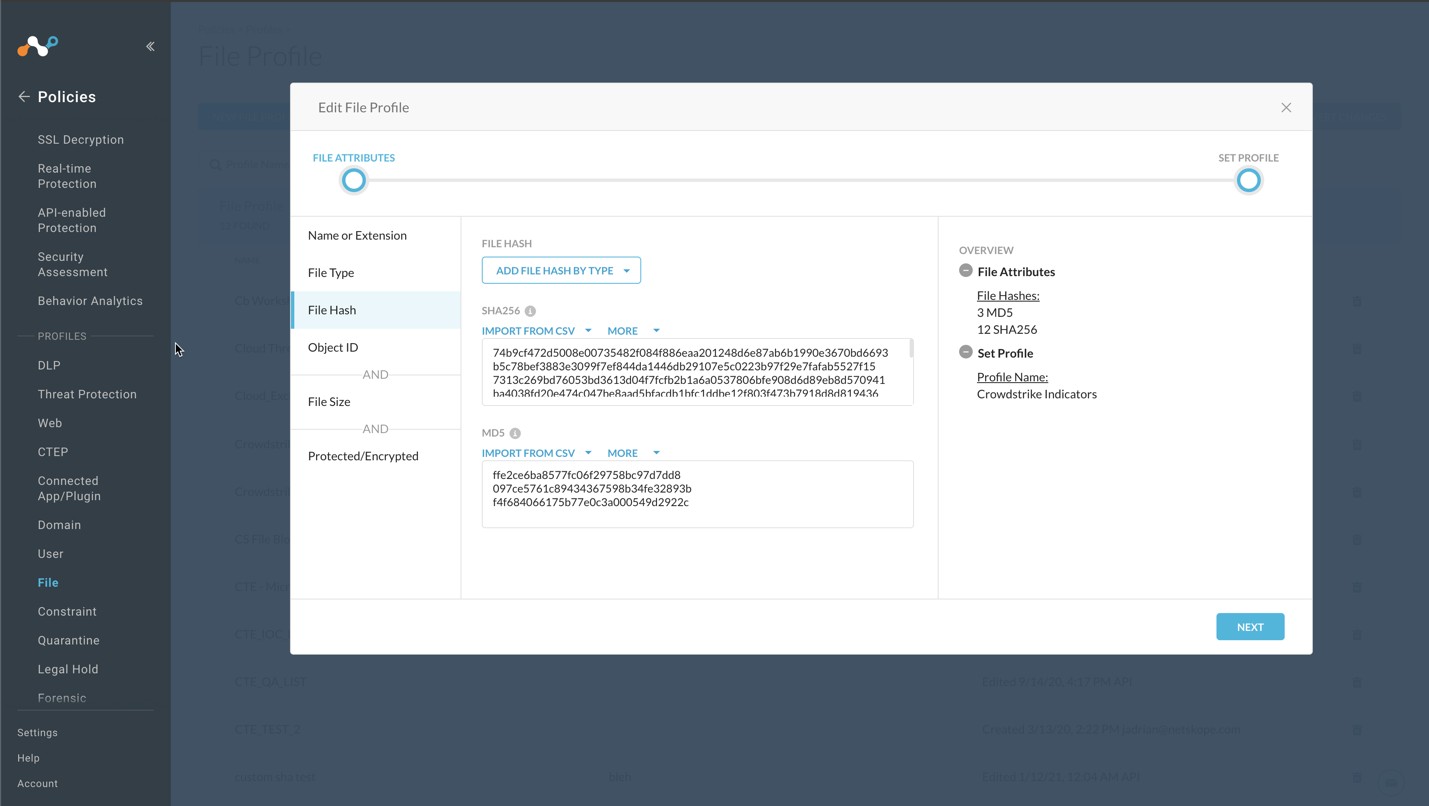
In your Netskope UI, go to Policies > File, select your custom File Profile, and click File Hash.
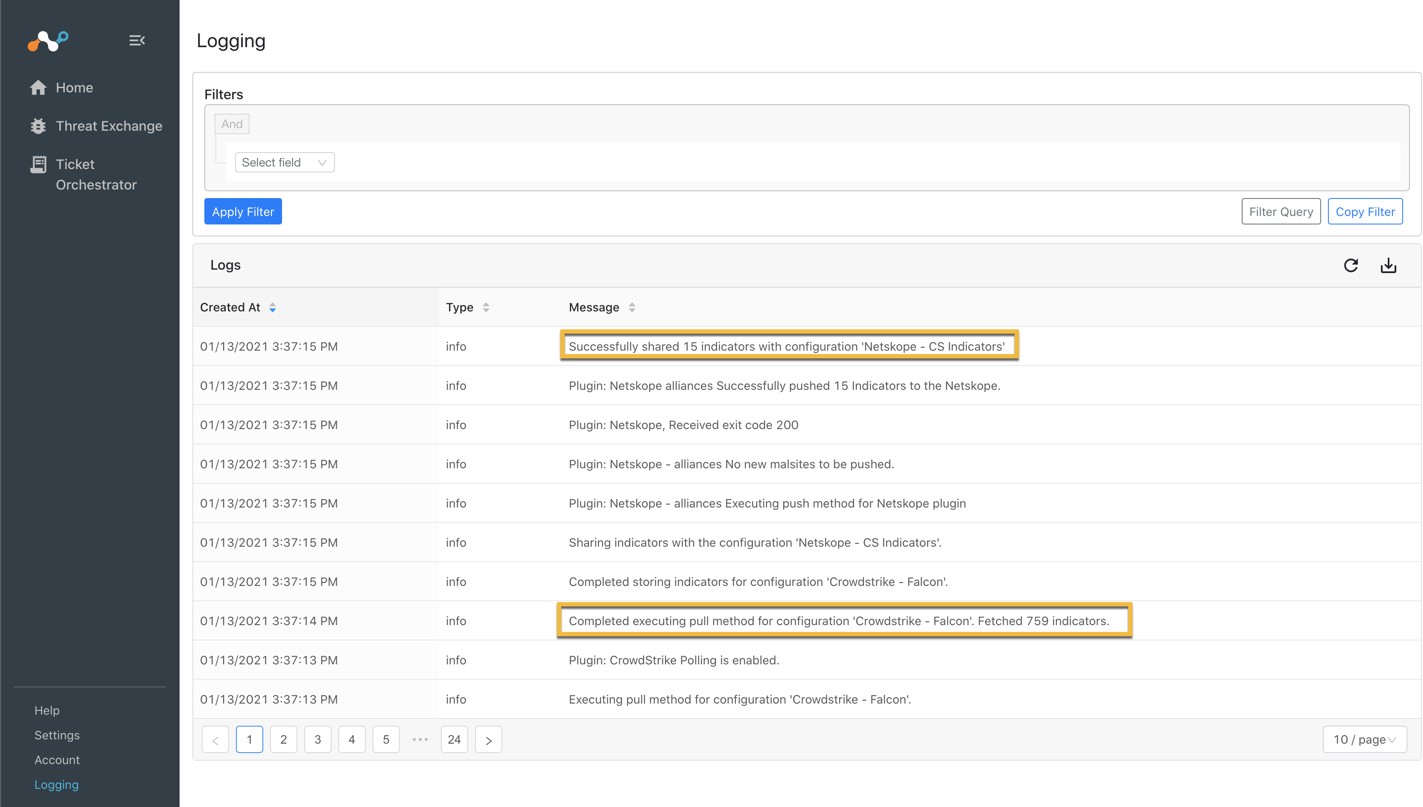
If data is not being brokered between the platforms, you can look at the audit logs in Cloud Exchange. In Cloud Exchange, go to Logging and look through the logs for errors.