Add Bypasses in Netskope
There are two types of bypasses when it comes to Netskope: Steering Bypasses and SSL Bypasses.
Bypass Types | Description |
|---|---|
Steering Bypass | Traffic is bypassed entirely from Netskope at the device level and is sent direct to the destination. It will never reach the Netskope Cloud. |
SSL Decryption Bypass | Applicable to Web and SSL/TLS encrypted traffic only. The traffic is sent to the Netskope Cloud, but bypassed from SSL Inspection. This can be useful when an application is certificate-pinned (and breaks when inspected), but you still want Netskope to attempt to filter and scan the traffic. |
It is recommended to use SSL Bypasses over Steering Bypasses where possible.
Important
We recommend using SSL Bypasses over Steering Bypasses whenever possible. Excessive steering bypasses can expose your organization to a higher risk.
Note
Netskope automatically maintains a bypass list of applications that employ SSL Certificate Pinning so that you don't have to add them yourself (like Crowdstrike, Dropbox, iCloud, etc).
This list can be reviewed under Settings > Security Cloud Platform > Steering Configuration. Select a steering profile and navigate to the Exceptions tab to review the bypassed application list.
SSL Bypasses
To add an SSL Bypass, go to Policies > SSL Decryption, and click Add Policy.
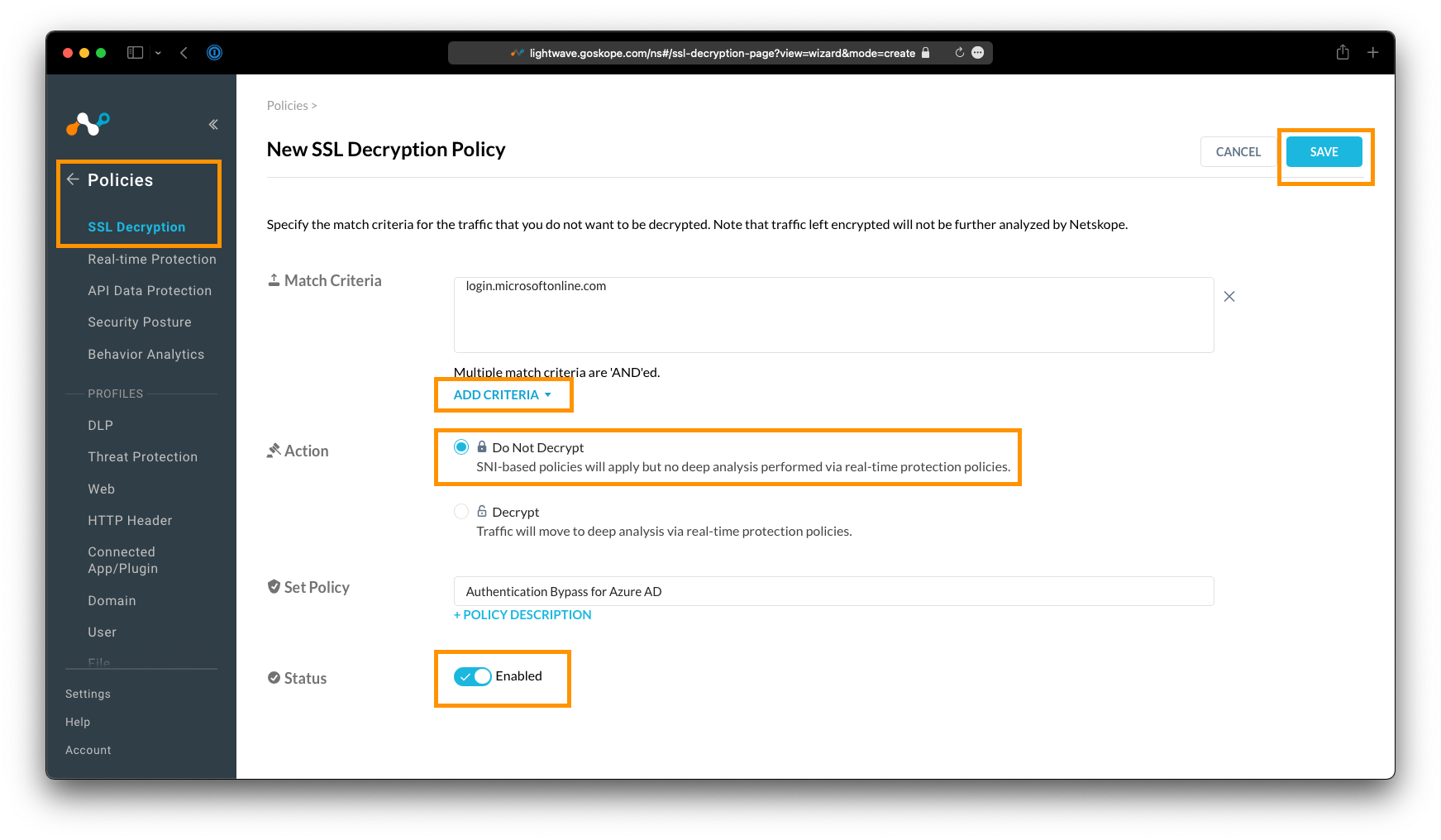 |
Adding a new SSL Bypass Policy. Multiple different criteria can be used.
On the New SSL Decryption Policy page, click the Add Criteria button. The following criteria can be used for an SSL Bypass:
Source Network Location: For example,
10.0.10.5/32,10.0.65.0/24Destination Network Location: For example,
1.2.3.4Category: For example,
FinanceUser: For example,
user@company.comUser Group: For example,
SSLBypassGroupOrganization Unit: For example,
MarketingApp Suite: For example,
AmazonApplication: For example,
Microsoft Teams.
Note
To define named Source and Destination Network Locations, go to Policy & Network Location, and create a new Network Location with your desired IP ranges.
Ensure you select the action Do Not Decrypt in order to bypass the above criteria from SSL Inspection.
Give the policy a name, ensure it is set to Enabled, and click Save.
Important
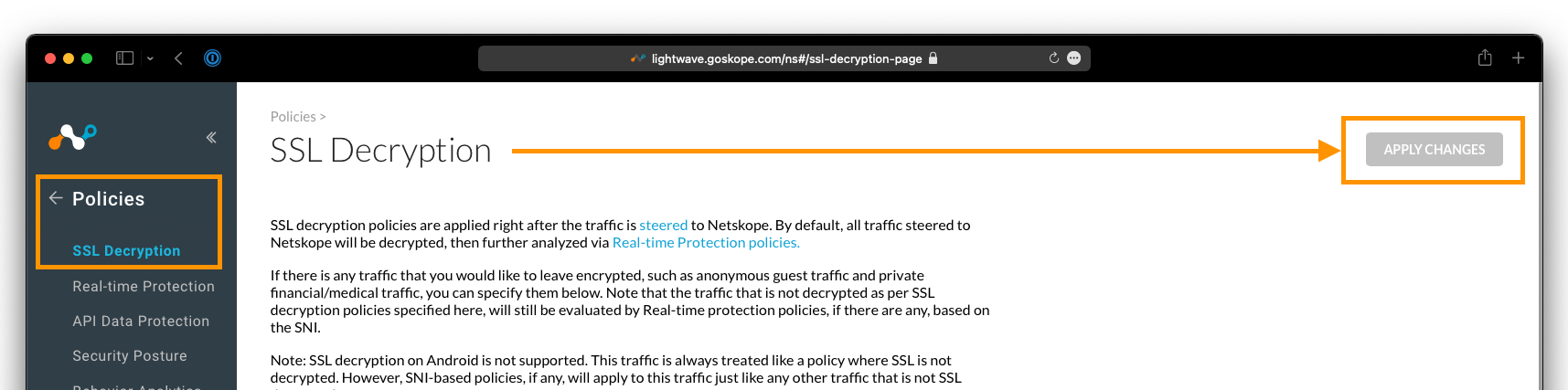
Don't forget to click Apply Changes under Policy > SSL Decryption once you have added a bypass. This is required for your changes to take effect.
 |
Steering Bypasses
To add a Steering Bypass, go to Settings > Cloud Security Platform > Steering Configuration, and click on the default tenant steering configuration (or any other steering configuration present) to make changes.
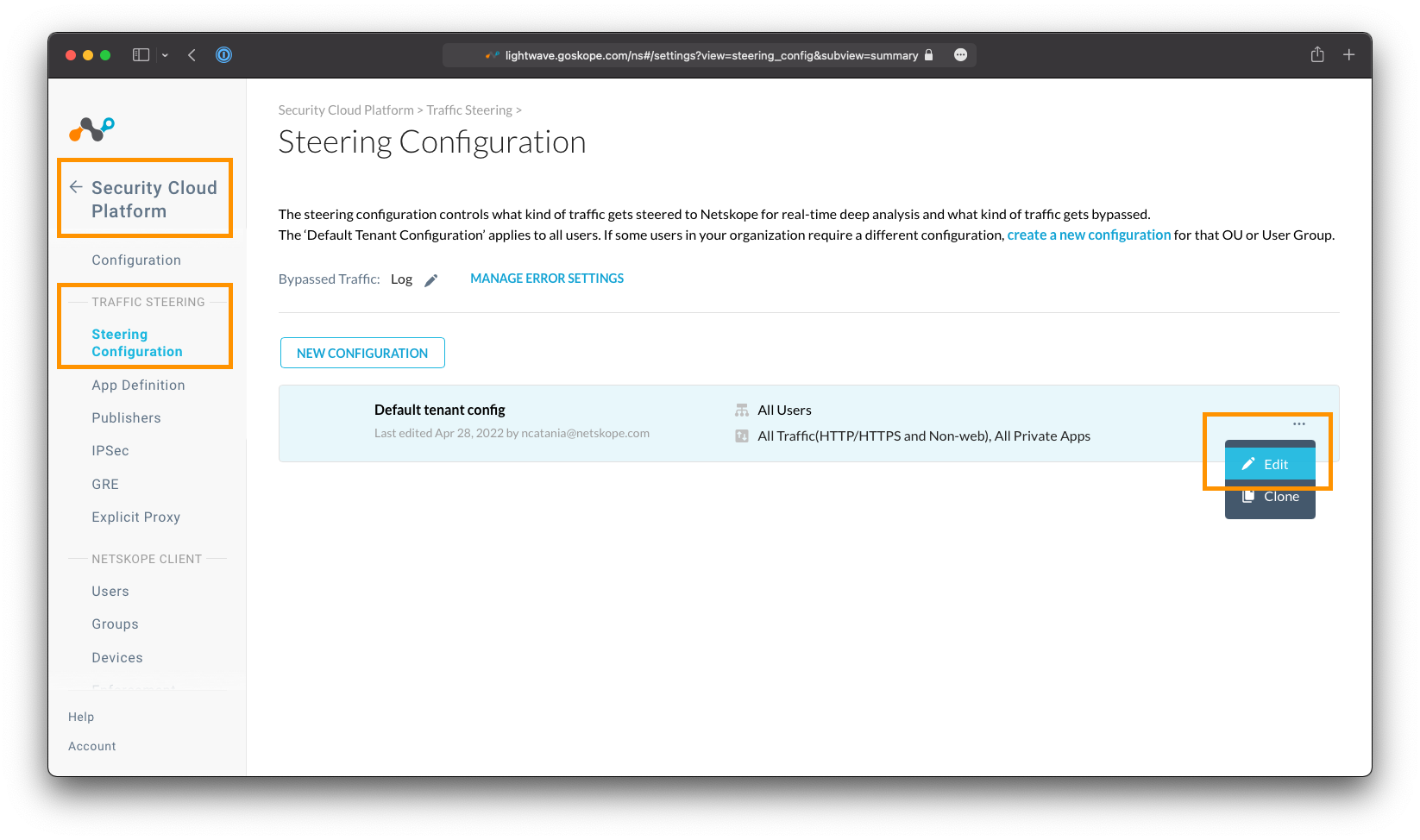 |
Steering Bypasses are added by modifying the steering configuration profiles assigned to the Netskope Client.
Click the Exceptions tab, then click New Exception.
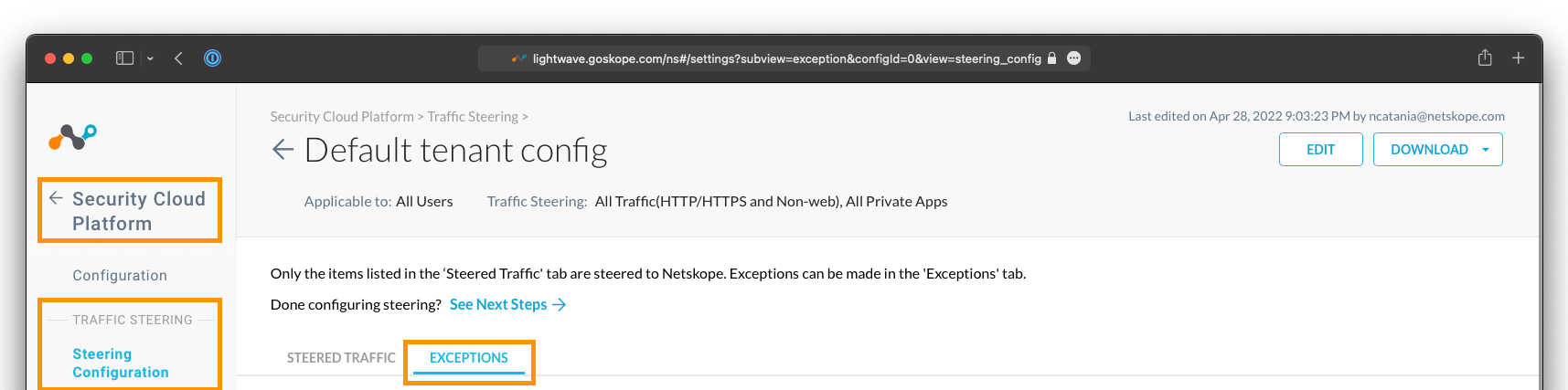 |
To add a steering exception, go to the Exceptions tab and click New Exception.
The following criteria can be used when adding a Steering Bypass:
Application: For example,
Microsoft TeamsCategory: For example,
FinanceCertificate-Pinned Applications: For example, the known apps that are certificate-pinned
Domains: For example,
app.company.comSource Locations: For example,
10.0.0.5/32,10.0.65.0/24Destination Locations: For example,
1.2.3.4Source Countries: For example,
China,Russia.
Note
To define named Source and Destination Locations, go to Policies > Network Location, and create a new Network Location with your desired IP ranges.
Steering Bypasses are added to a policy immediately and applied automatically to the Netskope Client on the next check-in (every 15 minutes).
Recommended Bypasses
Netskope recommends that you put the following bypasses in place at a minimum:
Bypass | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Authentication Bypass / SSO Login Page | Steering Bypass | A best practice is to bypass the URL of your SSO provider's login page. In certain scenarios where a user is connecting from an unmanaged device while on-premises, Netskope will redirect them to your SSO provider to determine their identity before allowing a connection. However, the redirect to the SSO provider will also be blocked, because they have not authenticated yet (causing a loop). This is typically a Domain-based bypass:
If you use Conditional Access policies, you MUST include this bypass or the traffic will appear to come from a Netskope IP address; potentially causing the Conditional Access policy to fail/deny access. |
VPN Gateways | Steering Bypass | Ensure that all of your VPN hostnames and destination IPs are bypassed from Netskope. If Netskope intercepts and inspects these connections, connectivity to the VPN is likely to fail. These bypasses will be both Domain based and Destination Network Location based. |
Endpoint (EDR) Agent / Client | SSL Bypass | Certain EDR vendors (like Crowdstrike) certificate pin the connections their agents make back to the cloud to prevent tampering. You should ensure that these are bypassed from SSL inspection. These bypasses will typically be Domain-based, like |