Validate Traffic Steering
Now that the Netskope Client has been deployed, check to confirm it is enabled, working, and correctly forwarding traffic to the Netskope Cloud.
Desktop Operating Systems
For Windows, macOS, ChromeOS, and Linux, if the Netskope client is running, you will see it located in the device's system tray or Menu Bar (look for the Netskope logo).
If the client is enabled and connected, the client icon will be colored 
If the client is disabled and disconnected, the client icon will be grayed out 
There are also variations of the icon may be displayed to indicate an error or fail close scenario. If the icon is missing, check the Start Menu or Application list on your device and check to see if the Netskope client is installed.
If the client is disabled, you can right-click on the icon and click Enable Netskope Client to have it connect and start forwarding traffic. Likewise, when connected, you can right-click and select Disable Netskope Client to turn the client off (depending on the Netskope Client settings you configured, this option (along with others) may not be present).
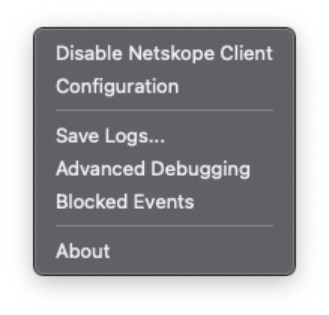 |
The right-click menu of the Netskope Client. Certain options may not be present based on your settings.
To check information about the Netskope connection and device profile, right-click on the Netskope Client icon and select Configuration. Here you will be able to see:
The authenticated user (traffic will be tracked as coming from this username) The Netskope gateway IP address and Netskope POP the user is connected to. Whether the device is currently marked as managed or unmanaged.
The Steering Configuration and Client Configuration profiles currently in use on the device.
The protocol used to tunnel traffic to the Netskope Cloud (like TLS, DTLS).
The last time the configuration of the Netskope client was updated. The Netskope Client will periodically phone home to check for updated configurations (this includes the notification messaged displayed to the user when a destination or activity is blocked).
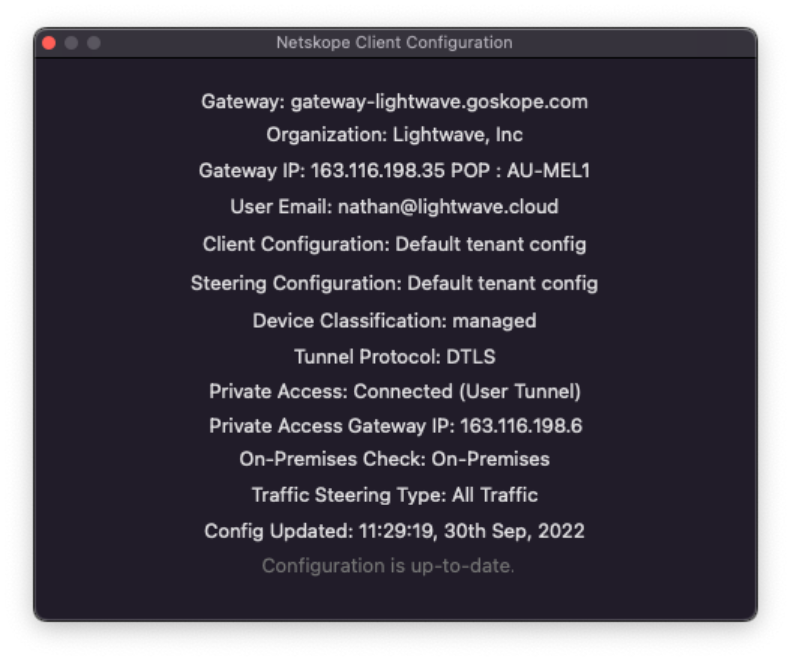 |
The Configuration panel of the Netskope Client shows relevant settings and connection information.
Mobile Operating Systems
For iOS and Android devices, check that a Netskope VPN profile has been installed and is enabled on the device.
If you wish to enforce the use of the profile and prevent users from disabling it, you will need to ensure to roll out the Netskope Client using a Mobile Device Manager (MDM), like Intune.
Tip
If you installed Netskope on the mobile device using an Email Invite, the Netskope certificate (required for SSL inspection) will be present on the device, but untrusted. You will need to tell the device to trust the certificate before browsing the web.
Failure to do will result in your browser throwing Insecure Connection or This Connection is not Private errors.
On iOS, go to Settings > General > About > Certificate Trust Settings and enable the certificate.
You will not need to do this if you installed Netskope via MDM.
Validate that the Netskope Client is forwarding traffic.
Open a new browser window and navigate to http://notskope.com or https://notskope.com (accessible over both HTTP and HTTPS). This website will tell you whether you are passing through the Netskope Cloud or not, and if so, which POP you are connected to.
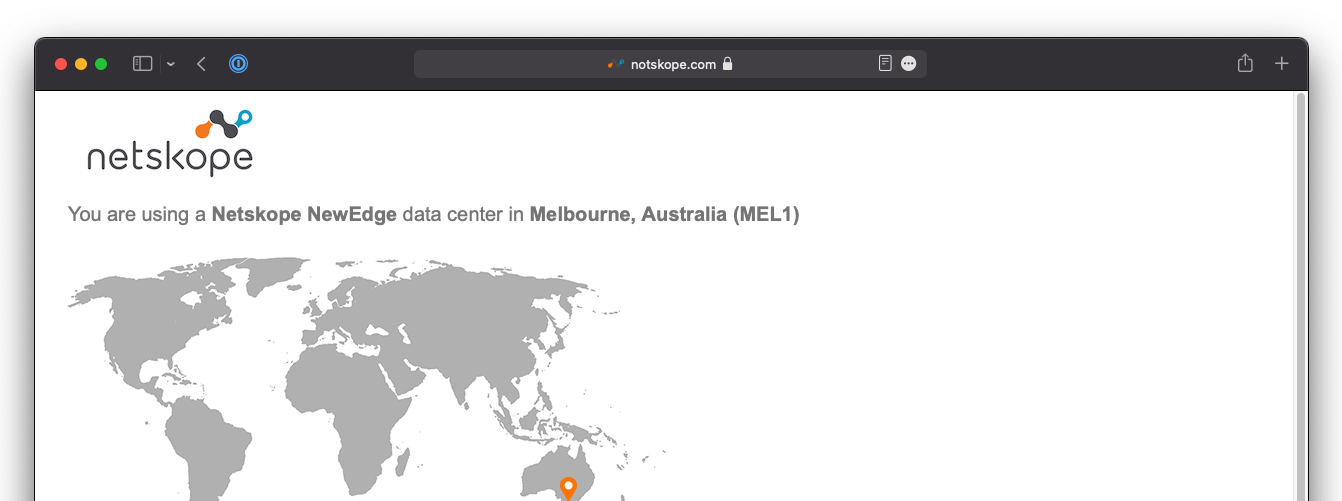 |
Netskope.com will tell you whether or not your traffic is reaching the Netskope Cloud, and the POP you are connected to.
If your connection does not load, try opening the page in a Private Browser or Incognito window to bypass the browser cache and try again.
To check whether content is being SSL inspected correctly, examine the certificate of https://notskope.com (or any other HTTPS site that isn't bypassed, like https://www.wikipedia.org). If the connection is being correctly SSL inspected, you will see an intermediate certificate with the name ca.<tenant-name>.goskope.com.
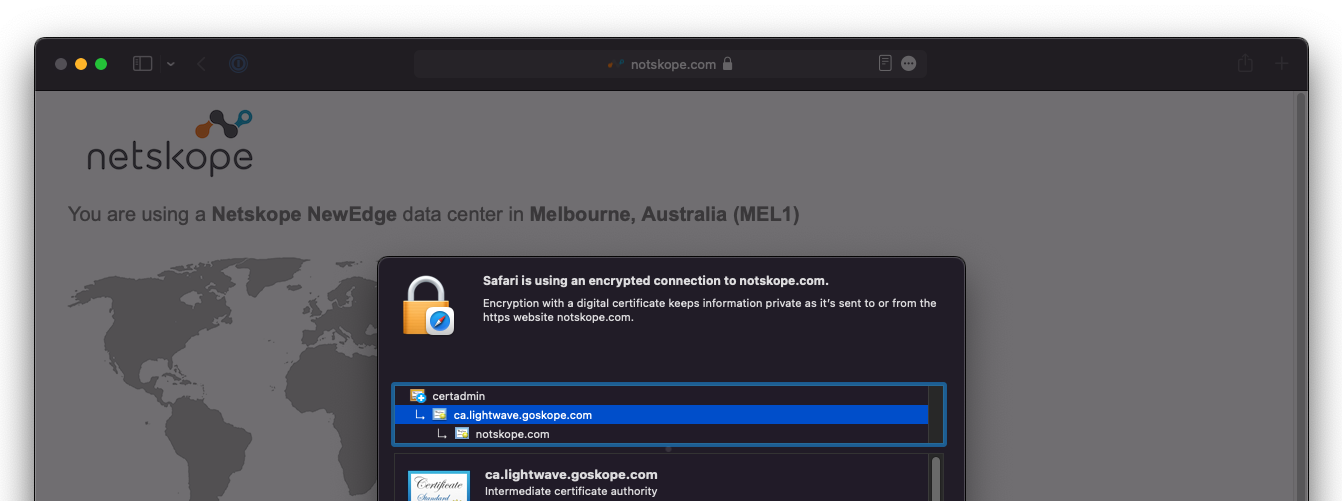 |
You can validate that a connection was SSL inspected by reviewing the certificate. If you see ca.<tenant-name>.goskope.com, en your connection was SSL inspected.
If this isn't present, then the connection is not being SSL inspected. You should check that there is not a steering bypass or SSL decryption bypass in place preventing this.
Installation and management of the Netskope root certificate is required for SSL inspection into the system certificate trust store, and the Firefox trust store is automated by the Netskope Client.
Important
Some thick/native applications (namely apps and tools used for development) use their own certificate trust stores to check certificate validity (like Git CLI, Azure Storage Manager, etc).
Internet connections over HTTPS using these apps will fail due to an untrusted SSL error; even through the Netskope root certificate is installed in the system trust.
In these scenarios, you need to manually install the Netskope root into the trust store used by the application. There is a community script available to assist with installation for the most common tools available here.
The Netskope certificate can be downloaded for distribution from Netskope tenant under Settings > Manage > Certificates. Click the Signing CA tab and download the Netskope Root Certificate (first option listed).